SEO Trends: What’s Shaping the Future of SEO
August 12, 2025
Introduction: The Ever-Evolving SEO Landscape
Sundar Pichai, Google’s CEO, recently stated that “Search itself will continue to change profoundly in 2025… you’ll be surprised even early in [2025] the kind of newer things search can do”.
This bold pronouncement underscores how rapidly search engine optimization (SEO) is evolving. What worked a year or two ago might not be enough today, as SEO trends shift with advances in technology and user behavior.
From the rise of AI-powered search results to the growing importance of user experience, staying ahead of these changes is crucial for anyone who wants to rank highly on Google.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the top 10 SEO trends of 2025 and offer tips on how you can adapt your strategy for each one. Short, digestible sections and clear examples will help you quickly understand what’s changing and how to respond. Let’s dive in and future-proof your SEO strategy for 2025 and beyond!
1. AI-Generated Content Goes Mainstream (But Quality Matters)
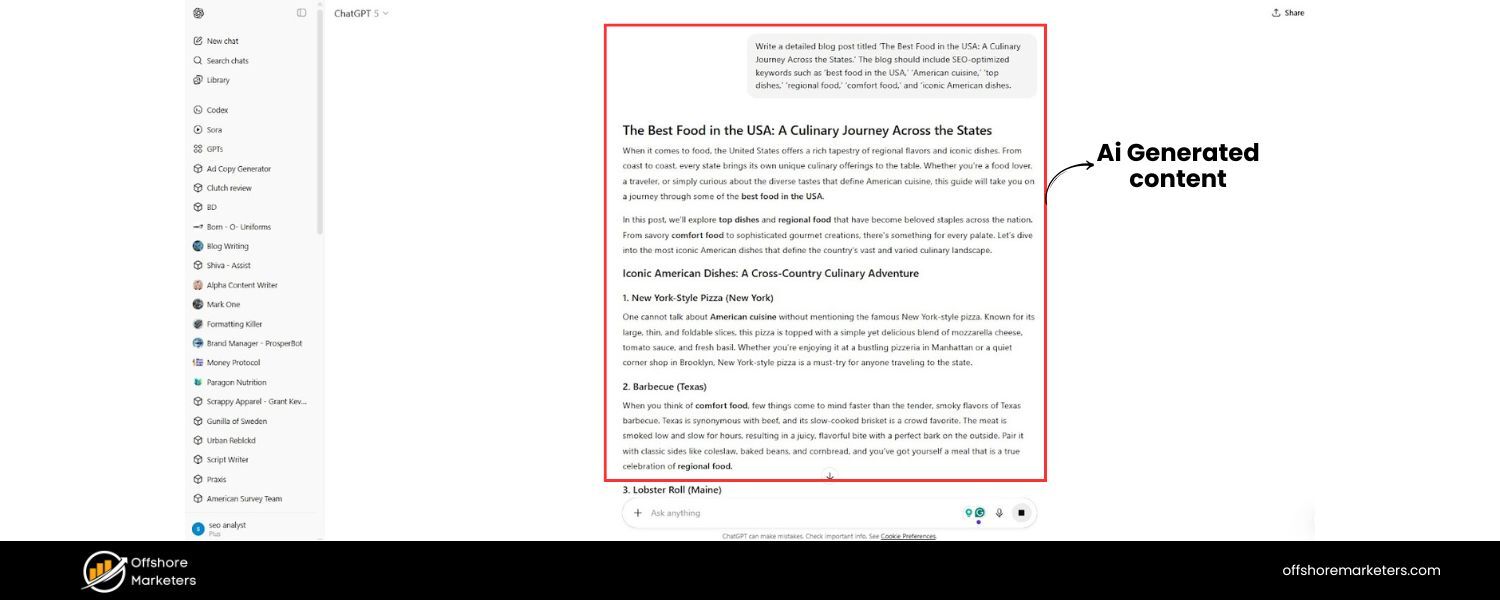
There’s no denying that artificial intelligence has stormed onto the content creation scene. Marketers are increasingly leveraging AI writing tools to generate blog posts, product descriptions, and more at scale. In fact, recent data shows that about 50% of marketers now use AI to assist with content writing.
This includes using AI for everything from brainstorming topics to drafting entire articles. The appeal is clear: AI can crank out content quickly, helping sites target more keywords and produce more posts than a human alone could.
A 2024 industry report found marketers are increasingly using AI tools for content creation, 50% are even using AI to write entire drafts, among other uses (as shown above).
However, more content doesn’t always mean better content. AI-written text often lacks the uniqueness, depth, and human touch that make content truly resonate with readers.
Google’s algorithms have been tuned to favor original, valuable information, not just a rehash of what’s already online. If everyone in your niche is using the same AI tools, there’s a risk that many articles start to sound the same.
Google has explicitly stated that adding unique insights and fresh perspectives is important for ranking. In other words, content needs E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) – a framework Google uses to assess quality – which purely machine-generated text may lack.
How to Adapt: Rather than letting AI run on autopilot, use it as a starting point. Generate first drafts or get content ideas with AI, then refine the output heavily. Inject your brand’s expertise, case studies, examples, and voice into the article.
This two-step approach marries AI efficiency with human quality control. For example, you might use an AI tool to outline a blog post or produce a rough draft, then revise it to add original research, anecdotes, and up-to-date data.
By doing so, you ensure the final content is unique and valuable to readers, which is exactly what Google rewards. In short, AI can help you scale content production, but the human touch is irreplaceable for creating content that ranks and engages.
2. AI-Powered Search Results and the Rise of Zero-Click Searches
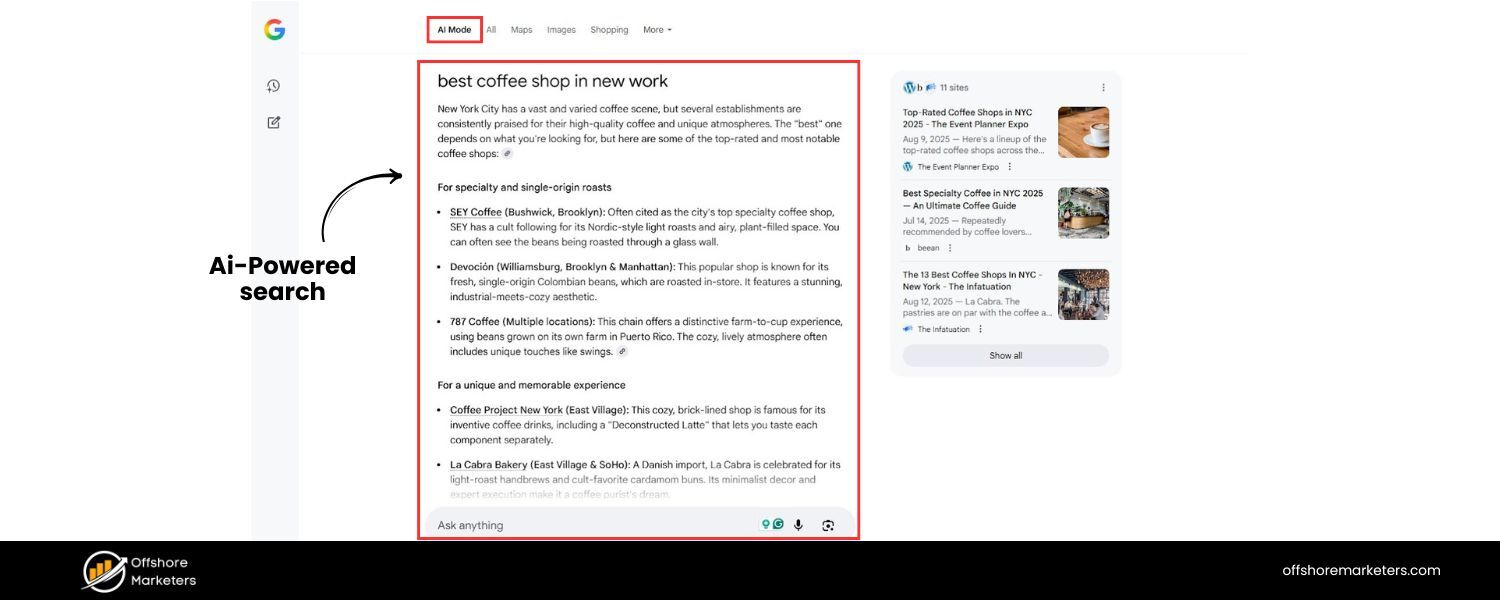
AI isn’t just changing how we create content – it’s also transforming the search results pages. Google’s introduction of the Search Generative Experience (SGE) is a game-changer. SGE uses generative AI to provide rich answer summaries right at the top of the results, often with no need to click a link.
Similarly, Bing’s integration of ChatGPT into its search interface means users can get conversational answers immediately.
These developments contribute to a growing trend: zero-click searches, where the user’s query is answered directly on the Google results page without requiring any further click-through.
This trend has been building for years with featured snippets, knowledge panels, and other instant-answer boxes. But AI overviews have supercharged it. Recent research from SparkToro suggests nearly 60% of Google searches now end without any click to a website.
In other words, more than half of searches give the user what they need on Google itself, via an snippet, map pack, definition, or AI-generated answer – and they never visit your page.
Additionally, early analyses of Google’s SGE indicate that these AI snapshots can significantly reduce organic clicks to websites (one report noted AI overviews might reduce clicks by 30% or more for affected queries).
For website owners and SEO professionals, the rise of zero-click searches means it’s more important than ever to earn a place in those on-SERP features. If your content provides an answer, you want Google to feature your snippet or cite your page in the AI overview.
It’s also a prompt to diversify the type of content you offer. Consider providing tools, calculators, or interactive content that give users a reason to click through. If basic questions get answered on Google, think about what deeper value you can provide that an AI snippet cannot, such as in-depth tutorials, videos, or personalized content.
How to Adapt
Optimize your content to appear in featured snippets and AI summaries. This includes formatting answers to common questions in concise paragraphs or bullet points (which Google can easily grab for a snippet), using schema markup to help define your content for search engines, and targeting long-tail question keywords.
Keep an eye on Google’s SGE (currently experimental) – if you’re in industries where it’s active, analyze how it presents information. Ensure that when an AI overview is generated, your site is among the trusted sources being cited.
Google has indicated it will prominently display sources in AI answers, including links to publishers’ sites. The key is to be one of those sources by publishing authoritative, well-structured content.
While you may not get every click, having your brand appear in the zero-click answers can still drive awareness and indirect traffic. And when you do get a click, make sure your page offers something extra (like depth, visuals, or interactivity) that justifies the visit.
3. Search Intent Optimization Is Non-Negotiable
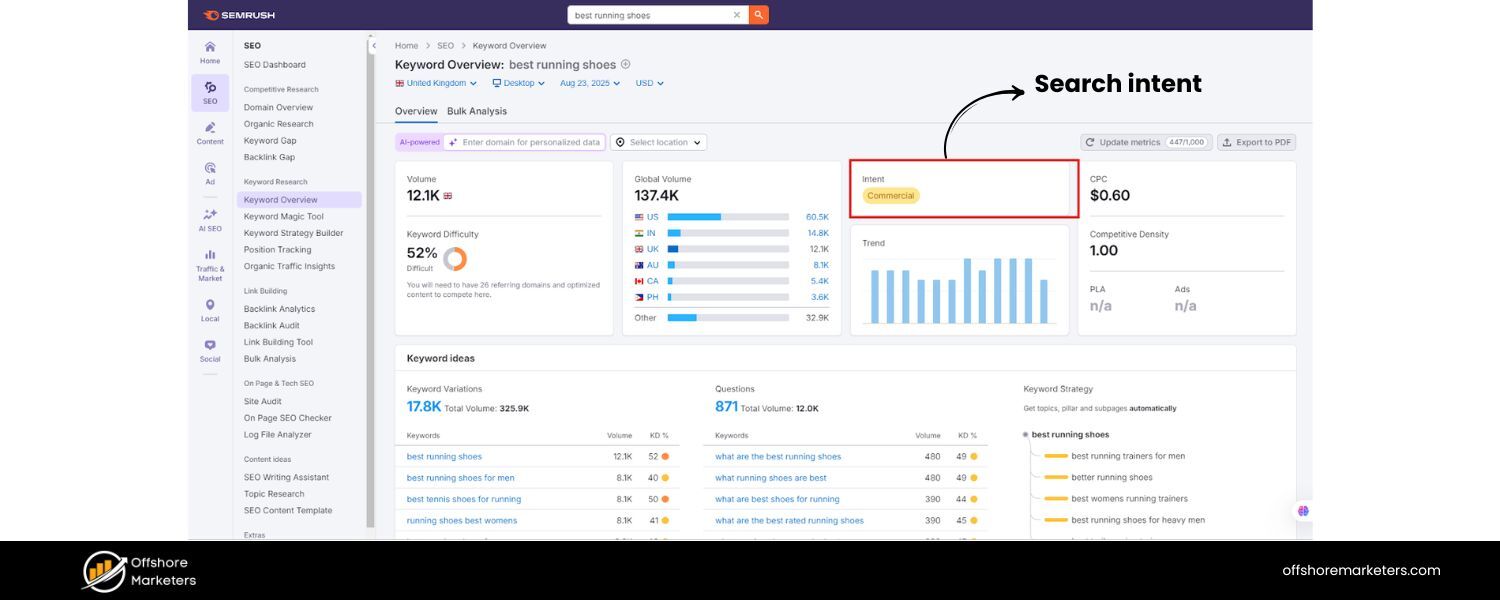
Matching user intent has long been a pillar of SEO, but in 2025 it’s truly non-negotiable. Google has become extraordinarily good at identifying what users are actually looking for, beyond the literal keywords they type.
As a result, content that precisely meets the searcher’s intent is dominating the rankings. If your page doesn’t satisfy the intent behind a query, it has little chance of ranking – no matter how many keywords you stuff into it.
Consider this example
A user searches for “best running shoes 2025.” The intent here is likely to research and compare options, not to land on a single product page. If a website tries to rank a product page for that query, it’s likely to fail because Google knows searchers want a list of top running shoes (with comparisons, reviews, etc.).
In fact, the top organic results for such “best” queries are almost always comparison listicles or reviews. We’ve all had the experience of clicking a search result and finding that the content isn’t what we expected – what do we do? We hit back and choose a different result.
Google tracks those signals (dwell time, bounce rate) as indicators of whether the intent was satisfied. If many users quickly leave a page, it likely didn’t give them what they wanted.
Google’s own ranking factor studies reinforce how crucial relevance is. Text relevance is currently the single most important factor correlated with higher Google rankings, according to a Semrush analysis.
In plain terms, this means your page needs to closely match what the user is looking for. Not somewhat match – exactly match.
A decade ago, you might rank with a generic article that tangentially touched a topic. Today, the content must be laser-focused on the query’s intent.
How to Adapt: Start every piece of content with intent research. Put yourself in the searcher’s shoes or use tools to identify the intent behind keywords (informational, commercial, transactional, or navigational).
A quick way to gauge intent is to simply Google your target keyword and see what types of pages are ranking. Are they how-to guides? Product pages? Listicles? Videos? The current top results reveal what Google believes satisfies users for that query.
Align your content format and angle accordingly. If the SERP is full of step-by-step guides, your page should probably be a step-by-step guide (and an even better one). If users want a tool or calculator, providing a static article won’t cut it.
Also, consider the specificity of intent. For instance, someone searching “how to fix leaky faucet” expects a tutorial (maybe with a video), whereas “leaky faucet causes” might indicate they want to diagnose the problem.
Tailor not just the content, but the depth and extras to what the searcher needs. Sometimes that means including a quick answer at the top (for the impatient searcher) and more details below (for the thorough researcher).
By satisfying search intent completely, you not only please Google’s algorithms but also delight users, which is the ultimate goal. Remember, a page that perfectly answers the query is more likely to earn longer visits, shares, and backlinks, creating a positive cycle for SEO.
4. User Experience (UX) and Core Web Vitals Are Essential for Rankings
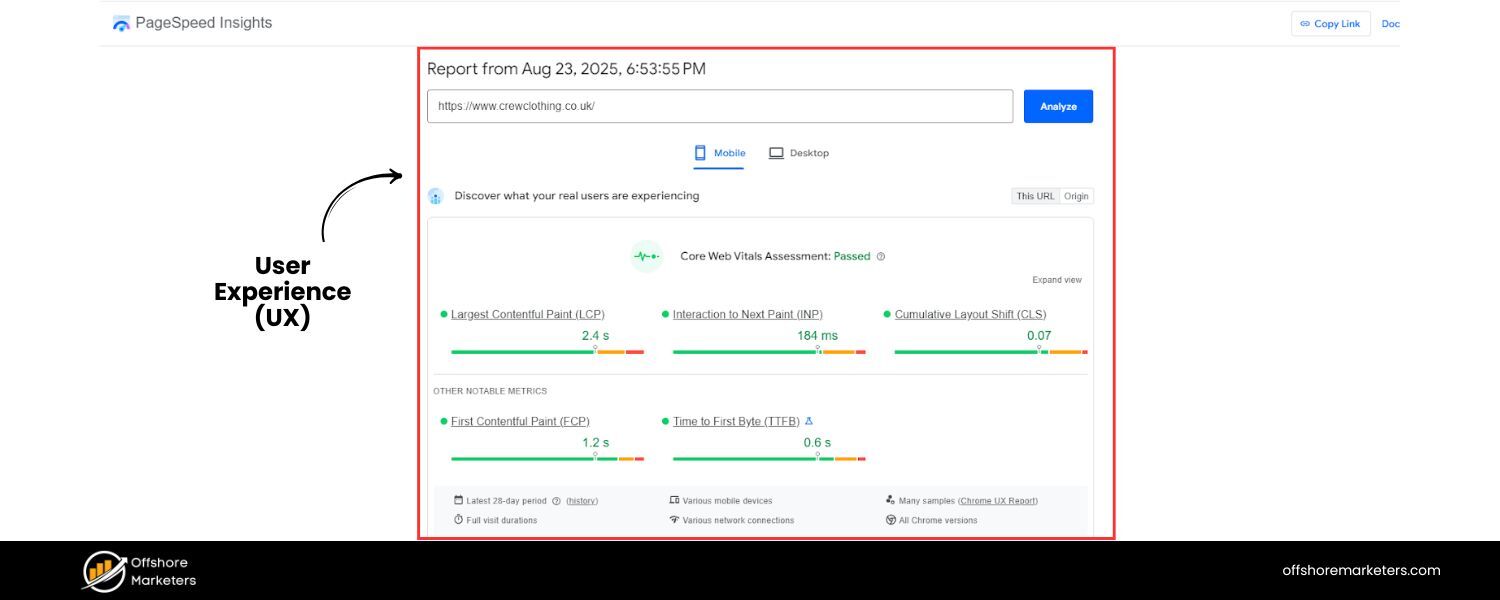
In 2025, SEO is not just about keywords and content – it’s about delivering a great user experience. Google’s push toward incorporating user experience signals into rankings has reached new heights.
We saw this with the rollout of Core Web Vitals as ranking factors (focusing on site speed, interactivity, and layout stability) and the continued emphasis on mobile-friendly design.
During Google’s 2023 antitrust trial, internal documents and patents even confirmed that user interaction signals (like click-through rate, time on site, pogo-sticking) influence rankings. The writing is on the wall: if your website frustrates users, Google won’t want to send traffic to it.
What does a good UX entail for SEO? It means pages that load lightning fast, layouts that are clean and mobile-responsive, and content that’s easy to read and interact with. It also means avoiding intrusive pop-ups or anything that causes users to bounce in annoyance.
Think of Google’s perspective: their goal is to give searchers satisfying results. If your page delights visitors (they stay for a while, scroll, maybe even convert), that’s a positive signal. If visitors consistently leave immediately, that’s a red flag.
Another aspect of UX is site structure and navigation. A well-organized site where users (and search crawlers) can easily find related content is likely to perform better.
Internal linking, clear menus, and logical content grouping help users seamlessly get more info – reducing bounce rates and increasing pageviews per session. All these behavioral metrics feed back into how search engines perceive your site’s value.
How to Adapt
Audit your site’s user experience with a fine-tooth comb. Use tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights to check your Core Web Vitals and address any issues (e.g., optimize images, enable browser caching, fix slow server responses).
Ensure your site is fully mobile-optimized – a huge portion of searches are mobile, and Google primarily uses mobile-first indexing. Simplify your page designs: use easy-to-read fonts, break up text with headings and bullet points (like we’re doing in this article!), and make important information stand out.
It’s also wise to monitor your user engagement metrics in Google Analytics (like bounce rate, time on page) as proxy indicators for UX.
If certain pages have very high bounce rates, ask why – is the content off-target, or is the page experience poor? Conducting A/B tests on elements like page layout or call-to-action placement can provide insights into what keeps users engaged.
In short, make your website a pleasure to visit. Not only will this help your SEO directly (through better rankings), but it will also increase conversions and the overall success of your site.
Google’s algorithm updates increasingly reward sites that put users first – so by prioritizing UX, you’re aligning your strategy with Google’s mission.
5. The Rise of Zero-Click Searches (Featured Snippets and AI Answers) – Continued
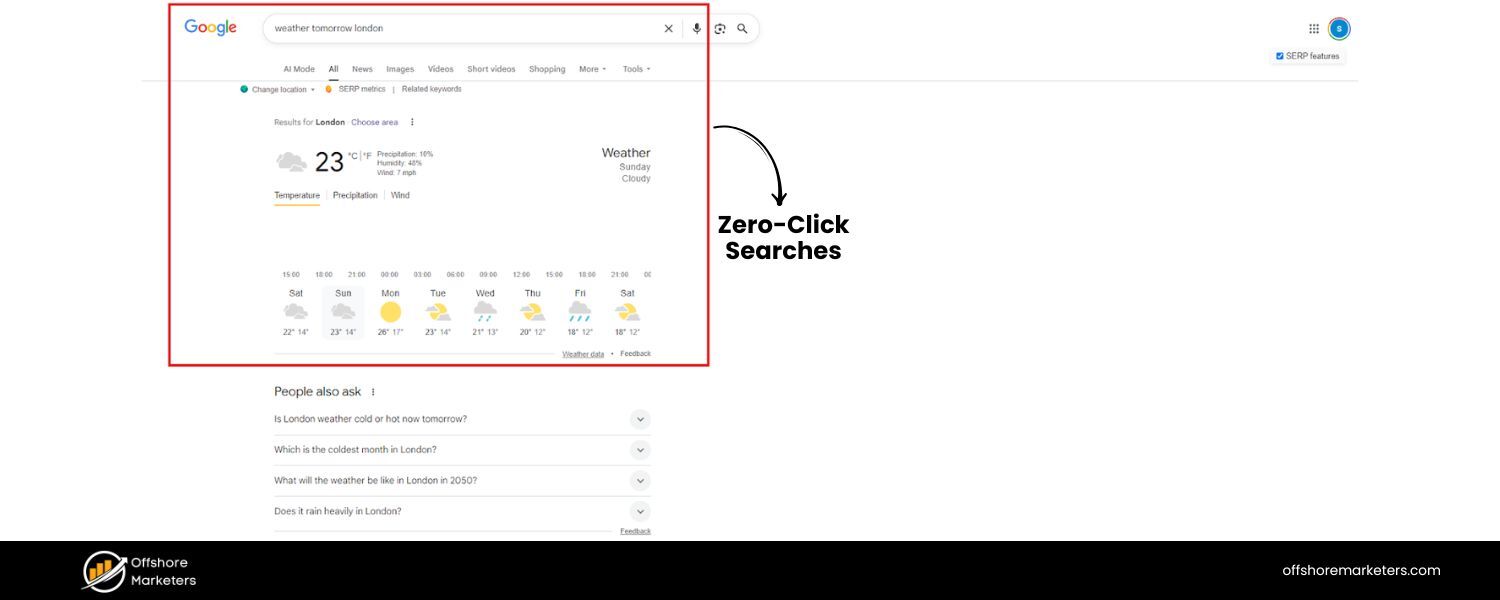
We touched on zero-click searches in the context of AI, but it’s worth emphasizing how significant this trend is on its own. A “zero-click search” is any search where the user doesn’t click through to a non-Google website.
This could be because Google provided the answer directly on the results page – via a featured snippet, knowledge panel, map result, calculator, or any other SERP feature. By 2025, zero-click searches have become extremely common, fundamentally changing the traffic patterns from search.
To reiterate the data point: nearly 60% of searches end without a click. For SEO, this means that simply ranking #1 may no longer guarantee you the bulk of the traffic if a large portion of users get what they need from the snippet above your result.
For example, if someone searches “weather tomorrow [your city]”, Google will show the weather forecast at the top – no click needed. Or if they search a factual question, an instant answer might appear.
Even searches like “best laptop 2025” might show a carousel of products or an AI summary that curtails clicks to individual review sites.
From a content perspective, this doesn’t mean SEO is dead – but it does mean we have to strategize differently.
One approach is to optimize for those snippets and rich results. If Google is going to show an answer, you’d prefer it be extracted from your site, complete with a link and attribution. Another approach is to identify queries where people will want to click for more detail.
Complex, in-depth, or creative queries often still require a click. In those areas, high-quality content can shine.
It’s also worth noting that brand presence and reputation become important in a zero-click world. If users see your brand name cited in an answer (even if they don’t click immediately), that can build trust and might lead them to seek you out later.
For instance, being featured as “Source: YourSite.com” in a snippet can be as good as the click in terms of branding.
How to Adapt
Optimize for featured snippets by structuring your content to directly answer common questions in your niche.
Use clear headings and concise answers (40-60 words) to Q&A style queries. Implement schema markup (structured data) wherever relevant – for example, FAQ schema, HowTo schema, Product schema – to increase your chances of getting rich results.
Track which queries your site currently appears for in featured snippets (Google Search Console’s performance report can help here) and double down on those opportunities.
Additionally, think beyond the click: provide value that goes beyond the basic answer. If a search result is likely to be answered on-page, consider what follow-up question the user might ask next, and cover that in your content. This way, even if the initial answer is given by Google, the user has a reason to click your site for the deeper dive.
For example, a snippet might list the top 5 running shoes in a carousel, but your article can provide the full comparison, pros and cons, and user reviews that a one-line answer cannot.
By anticipating user needs and delivering content that complements the instant answers, you can still win traffic and engagement in the era of zero-click searches.
6. E-E-A-T and Brand Authority Are More Important Than Ever

Google’s quality algorithm revolves heavily around the concept of E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. In 2022, Google even added an extra “E” (for Experience) to this framework, underlining the importance of content created from first-hand experience.
In 2025, demonstrating E-E-A-T is not optional – it’s a must, especially in competitive niches like health, finance, or any Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) topics where trust is critical.
One manifestation of this trend is the increasing weight given to author reputation and brand presence. Google favors content from sources that are known to be authoritative on a topic.
This is why a well-established site or a recognized expert often outranks a newbie publishing the same information. As one SEO expert noted, “Users and search engines prioritize trusted brands, so consistent branding and high-quality content are essential.”.
In practice, this means building your site’s authority through quality over quantity: 10 great articles that people reference and share are better than 100 mediocre ones.
Brand presence across the web is also acting as an authority signal. This goes beyond just backlinks. If your brand is frequently mentioned (in a positive context) on forums, social media, news sites, etc., it can indirectly boost your credibility in Google’s eyes.
It’s akin to offline reputation – the more people cite you as a trustworthy source, the more weight your own content carries.
Google’s own Quality Rater Guidelines (which, while not algorithmic, indicate what Google cares about) emphasize finding out who the author of content is and evaluating their credentials.
They also stress looking for signs of trust: are there references and citations? Is the content transparent about sources? Does the site have clear contact info and a good reputation? All these factors play into E-E-A-T.
How to Adapt
Make sure every piece of content you publish showcases expertise. This could mean having it written or reviewed by someone with credentials (and stating those credentials in an author bio). For example, if you run a medical blog, having an MD review articles and listing their name and profile adds a ton of credibility.
Cite reputable sources to back up facts – just like we’re doing in this article with external citations. This not only bolsters trust with readers but also with Google’s algorithms that can recognize references to authoritative domains.
On the site level, create a robust About page that highlights your team’s expertise and experience. Encourage happy customers or readers to leave reviews and testimonials on platforms that matter (Google Business Profile for local, Trustpilot, industry forums, etc.).
Consistent branding is key: use the same name, logo, and tone across all your online presence so that signals coalesce around one entity – your brand. Over time, as your site accumulates quality content and positive mentions elsewhere, your authority will snowball.
This pays off in higher rankings, as Google will be more likely to trust your content as the best answer for relevant queries.
In short, treat your website like a thought leader in its field. Don’t just chase trending keywords; publish genuinely insightful content that others will want to reference.
Build relationships in your industry (guest post on reputable sites, collaborate with known experts). All these efforts signal to Google that you are a trustworthy authority – which is ultimately rewarded with better visibility.
7. Diversification: Beyond Google- SEO for Other Platforms
While Google is still the dominant search engine, 2025 has seen a notable shift: people are increasingly searching for information beyond the traditional search engines.
Savvy marketers are paying attention to alternative search platforms, from Bing and DuckDuckGo to platform-specific searches on YouTube, Amazon, and even social media. In fact, Google itself revealed a startling insight: “In our studies, something like almost 40% of young people, when they’re looking for a place for lunch, they don’t go to Google Maps or Search. They go to TikTok or Instagram,” according to a Google executive.
Generation Z, in particular, often treats TikTok, Instagram, or YouTube as their search engines of choice for certain queries (e.g., product reviews, how-to videos, local spots).
What does this mean for SEO?
It means the definition of “search engine optimization” is broadening. If you’re only focusing on Google web search, you might be missing out on where a chunk of your audience is actually searching.
YouTube SEO is now a critical component for reaching users who prefer video content – YouTube is the world’s second-largest search engine by query volume.
Similarly, if you run an e-commerce business, optimizing for Amazon search might be as important as Google, since many shoppers go straight to Amazon to find products.
Bing’s rise is also worth noting. With the integration of AI (via OpenAI’s tech) into Bing, Microsoft gained some renewed attention.
While Bing’s market share is still much smaller than Google’s, it powers Yahoo and DuckDuckGo under the hood, and with Windows integration, it’s not negligible.
Moreover, mentions in AI assistants and chatbots (like Bing’s chatbot, or even Siri and Alexa voice search) often pull from Bing’s index. We’re approaching a world where SEO is not just about Google’s 10 blue links, but about being visible wherever people search for information.
How to Adapt: Expand your optimization efforts to other platforms. Here are a few tips:
A. YouTube SEO
If you have content that could be in video form, create a YouTube video for it. Optimize video titles, descriptions, and tags with relevant keywords.Engagement signals (views, likes, comments, watch time) influence YouTube’s algorithm, so high-quality, engaging videos will perform better. Also, embed videos in your blog posts (and vice versa) to create a multi-channel presence.
B. Social Media Search
Understand that hashtags and keywords matter on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and LinkedIn as well.For example, on TikTok, ensure your description and on-screen text include the key terms someone might search for. Build content that aligns with what’s trending on those platforms to capture discovery traffic.If you’re a local business, don’t neglect platforms like Google Maps (Google Business Profile), Yelp, or even niche directories – many users go straight to those apps to search.
C. Bing and Others
Optimize your site for Bing by making sure you’re on Bing Webmaster Tools, and that your site follows solid technical SEO (which usually covers both Google and Bing’s requirements).
One interesting twist:
Bing places relatively more emphasis on social signals and Bing also has its own AI chat that might quote sources. So ensure your content is high-quality and perhaps keep an eye on Bing’s guidelines for their AI integration.
D. Voice Search
With voice assistants, queries tend to be more conversational (e.g., “What’s the best Italian restaurant near me?”).Optimize some content for long-tail, question-based phrases. Also, having an FAQ section in natural language can help capture voice query traffic. Keep your Google Business Profile updated, as voice searches for local info (hours, contact) are common.
The key takeaway is to meet your audience wherever they are searching. By broadening your SEO strategy to include other platforms, you increase your overall visibility.
Plus, success on one platform can often feed another, for instance, a popular YouTube video might earn backlinks to your site, boosting your Google SEO. Or strong brand social profiles might rank on Google for your name, giving you more real estate on the results page. It’s all interconnected, and a holistic approach will serve you best.
8. Visual Search and Video SEO Gain Traction
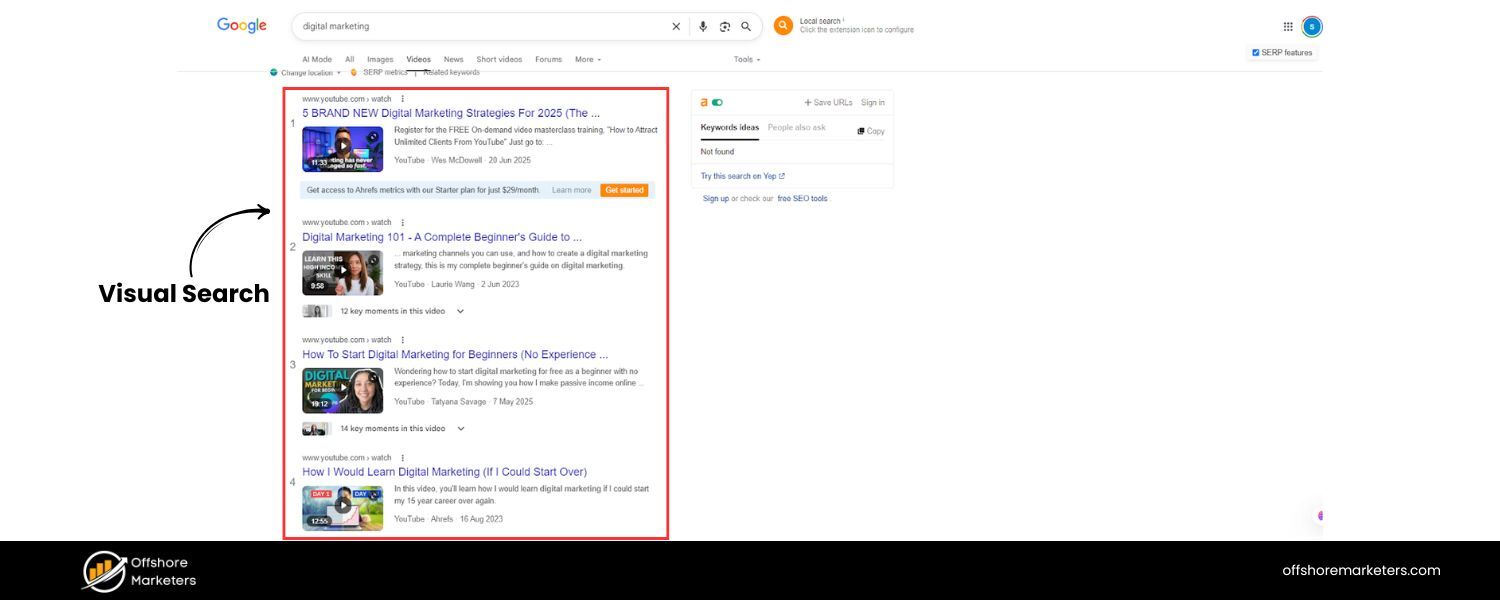
The adage “a picture is worth a thousand words” is becoming true in search as well. Visual search technology has improved dramatically – tools like Google Lens allow users to search using images or photos from their camera.
Google’s AI advancements now enable “multisearch,” where a user can combine image and text in a single query (for example, taking a picture of a dress and adding “green” to find that dress in green color). With billions of visual searches happening, optimizing for image-based discovery is an SEO trend you can’t ignore.
Likewise, video content is surging. Not only are platforms like YouTube and TikTok extremely popular, but Google also often features video results prominently for many queries (especially how-tos, tutorials, reviews, etc.).
Users increasingly prefer a quick video explanation for certain topics instead of reading text. The demand for video is such that one SEO forecast noted “videos, in particular, are set to play a crucial role in SEO strategies” because they provide authentic, human content that AI can’t easily replicate.
For visual search, think about the scenario: a user might take a photo of a product or a plant or a landmark and want information on it.
If you have an e-commerce store, ensuring your product images are optimized (with descriptive file names and alt text) can make them more likely to appear in Google Images or be identified by Google Lens.
Google can now identify objects in images and connect them to search intent. For instance, snapping a picture of a type of sneakers could lead the user to shopping results for that sneaker. You’d want your site’s image to be part of that result.
For video, beyond just making videos, you should also optimize them for search. This includes transcripts (which you can also turn into blog content), engaging thumbnails, and structured data like VideoObject schema on your pages. Remember that YouTube results can also appear on Google’s main SERP. Google often shows a video carousel for queries prefixed with “how to,” “review,” or anything that suggests a visual component.
How to Adapt
Ensure every image on your website is optimized with descriptive alt text and file names (e.g., red-running-shoes-nike.jpg rather than IMG_1234.jpg). Alt text not only helps with accessibility but also tells search engines what the image contains.
Submit an image sitemap if images are a big part of your site. If you’re in a niche like fashion, home decor, food, or travel – high-quality images and Pinterest-style SEO can drive significant traffic.
Leverage Google Images and Pinterest as search engines in their own right. For example, posting your images on Pinterest with proper descriptions and tags can get you visibility on Pinterest’s search (and Google Image search, since Pinterest images often rank well).
For videos, if you haven’t already, start incorporating video into your content strategy. A few ideas: product demos, explainer videos, interviews, webinars, how-to guides, or even quick tip-of-the-day videos. Host them on YouTube for the broadest reach. Optimize video titles and descriptions with keywords (without spamming).
A pro tip include the keyword at the start of your video title and say it in the video, YouTube’s transcription will catch it. Use chapters in YouTube descriptions for longer videos to target multiple search terms (each chapter can rank for different queries).
Additionally, embed videos on relevant pages of your site. This can increase time-on-page (a user might watch the video while on your page) which is a positive engagement signal. It also provides a richer experience, catering to those who prefer video over text.
In summary, visual SEO (images and videos) is no longer an afterthought. It’s becoming central. As AI makes information retrieval more seamless across media types, the lines between web, image, and video search are blurring. Cover all your bases by optimizing content in all formats.
9. Hyper-Focused Keyword Research and Long-Tail Targeting
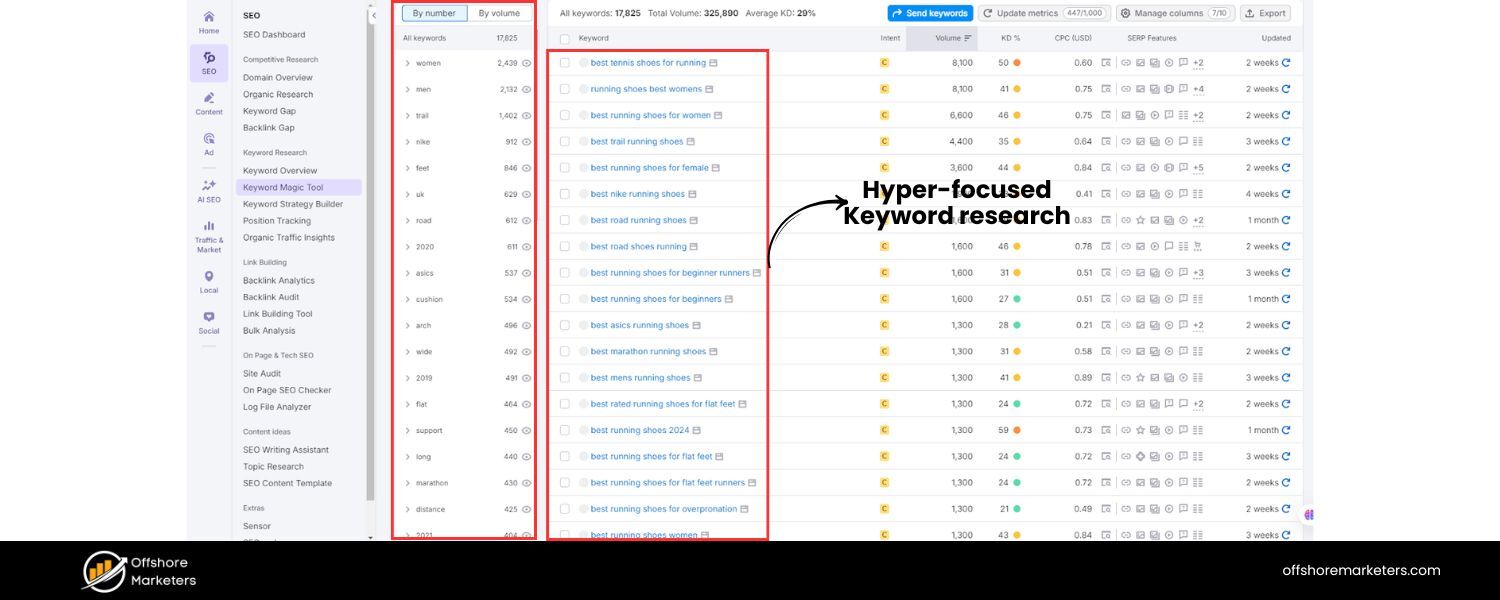
As the SEO landscape gets more competitive, a shotgun approach to keywords isn’t as effective. The trend is moving toward hyper-focused keyword research – identifying very specific, intent-driven keywords (especially long-tail phrases) that align with niche audiences or subtopics.
Targeting these can be goldmines for traffic, particularly for newer or smaller sites that can’t yet compete on broad terms.
One reason is that generic keywords are often dominated by big players or have ambiguous intent. Long-tail keywords (e.g., “best trail running shoes for flat feet in winter”) have a clearer intent and often a more conversion-ready audience. They also tend to have less competition.
A Semrush study pointed out that focusing on long-tail, specific search phrases is “even more crucial for brands with smaller or newer websites” – it’s a way to find pockets of opportunity where you can actually rank.
Moreover, with voice search and more natural language queries on the rise, people are searching in full questions or detailed phrases now. Instead of just “coffee maker,” someone might ask, “what’s the best drip coffee maker under $100 for small kitchens”. These extended queries are essentially long-tail searches. If you’ve got content tailored to that, you can capture those visitors.
We’re also seeing a shift from just “keywords” to topics and entities. Google’s semantic search capabilities mean it understands the relationships between topics.
But doing keyword research at a granular level helps ensure you cover subtopics that might otherwise be overlooked. For example, a broad topic like “SEO trends” can be broken down into subtopics like “AI in SEO,” “zero-click searches,” “Core Web Vitals,” etc.
By targeting the long-tail keyphrases around each subtopic (like “how AI is used in SEO content creation”), you cast a wider net.
How to Adapt
Refresh your keyword research process. Don’t just go after the head terms with the highest volume – include plenty of longer phrases that indicate specific needs or questions.
Tools like AnswerThePublic, AlsoAsked, or even Google’s “People Also Ask” box are great for uncovering common questions in your niche. Each of those questions can be a long-tail keyword to target with a section of a blog post, or a full blog post on its own.
When creating content, consider making comprehensive guides that naturally rank for hundreds of long-tail terms. For instance, an ultimate guide on “running shoes” could have sections for different foot types, terrains, budgets, etc.
Each section might grab a long-tail query. Use semantic SEO techniques: include LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords and related terms that give depth to the content. This isn’t keyword stuffing, it’s about thorough coverage of a topic.
If you operate in a local or niche market, incorporate local qualifiers or niche jargon as relevant. A small local bakery could target “gluten-free birthday cake bakery in [City]” rather than just “bakery [City]”. The volume might be lower, but the conversion intent is high, and the competition is lower.
Another tip: regularly review your analytics and Search Console data for the actual queries bringing people to your site. You might discover new long-tail terms that you haven’t explicitly optimized for yet. If they’re bringing traffic with little effort, imagine what a targeted article could do.
In summary, don’t underestimate the long tail. It’s where a lot of incremental gains can be made. By being hyper-focused in your keyword targeting, you can gradually build a strong presence that bolsters your site’s authority, which in turn will help you compete for the bigger terms down the line.
10. Continuous SEO Testing and Adaptation is Key
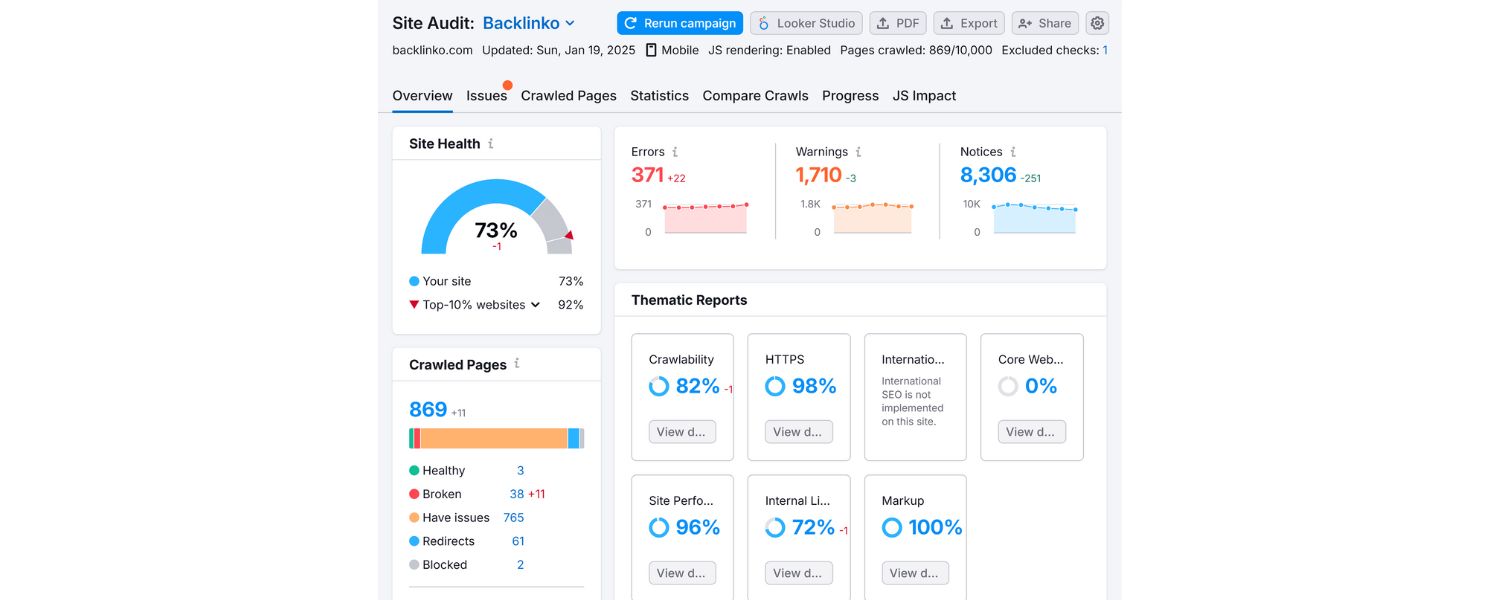
If there’s one trend that underpins all others, it’s that the only constant in SEO is change. Google updates its algorithms frequently (major core updates happen several times a year now, with countless minor tweaks in between).
New features appear on the SERP, user behaviors shift, and competitors are always on the move. In 2025, SEO is not a “set it and forget it” game – it requires continuous testing and adaptation.
We’re seeing more businesses embrace an experimental mindset with SEO. Instead of relying solely on best practices, they are running A/B tests on title tags, trying different content formats, experimenting with new link-building tactics, and more.
As one industry article noted, “expect to see a surge in businesses experimenting with different approaches and tweaks to their websites in an attempt to beat the competition”. The idea is to find what truly works for your site and your audience, which might differ from general wisdom.
For example, maybe the conventional wisdom is that shorter titles (60 characters or less) are best, but you find through testing that a slightly longer, descriptive title gets a higher click-through rate from Google for your articles. Or perhaps a certain call-to-action phrasing on your meta description boosts clicks.
Testing can reveal these insights. Likewise, you might test content changes: does adding an FAQ section improve rankings? Does restructuring an article with more subheadings reduce bounce rate? SEO intersects with user experience here – sometimes what pleases users (as evidenced by engagement metrics) ends up pleasing Google too.
Another dimension of adaptation is staying educated. Following SEO news (like Google’s Search Central Blog, industry blogs, and credible SEO Twitter accounts) can give you early warning of big changes (for instance, an upcoming change to how Google handles meta descriptions or a new “helpful content” update). Those who adapt quickly can turn algorithm shake-ups into opportunities rather than setbacks.
How to Adapt: Build a culture (even if it’s just you, make it a personal habit) of ongoing optimization. Some practical steps:
A. Regular Audits
Schedule SEO health checks quarterly (if not monthly). This includes technical audits (checking for crawl errors, broken links, page speed issues) and content audits (updating outdated information, improving underperforming pages). The goal is to catch issues and opportunities early.
B. Monitor and Measure
Keep a close eye on your key metrics – not just rankings, but also organic traffic, click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates from organic, and engagement metrics.If you see a sudden drop or spike, investigate it. Use tools that can alert you to significant ranking changes or downtime.
C. Implement SEO Testing
You can use more advanced techniques like SEO A/B testing (there are tools that allow serving different versions of a page to users to compare outcomes), or you can do simpler before-and-after tests.For example, change a title on a page and see if CTR improves over the next few weeks compared to the previous few. Change one thing at a time per page so you can attribute any change in performance to the likely cause.
D. Stay Informed
Dedicate some time each week to read up on SEO updates. The competitors and sources we analyzed for this article (like Search Engine Land, Search Engine Journal, Backlinko’s blog, Google’s own documentation, etc.) are great places to start.Understanding the “why” behind changes will help you adapt your strategy intelligently rather than just reacting blindly.
E. Be Ready to Pivot
If a certain tactic isn’t yielding results after ample time and effort, be ready to try something new. For instance, if you spent months building low-quality directory links (which might have worked 10 years ago but not now), recognize the sunk cost and pivot to a content-and-outreach strategy for backlinks. Agility is a strength in SEO.
By adopting a mindset of continuous improvement, you’ll make your SEO strategy resilient. Algorithm changes or new trends won’t knock you off course because you’ll already be in the habit of learning and adjusting.
This proactive approach is what separates sites that thrive from those that stagnate. In the race for organic visibility, the winners are usually the ones who iterate the fastest and most effectively.
Conclusion: Stay Agile and Keep the User at the Center
The SEO trends of 2025, from AI-driven everything to the primacy of user experience and authoritative content, all point toward one overarching theme: search engines are getting better at rewarding the sites that best serve their users.
To rank among the top results, we need to align our strategies with that goal. That means embracing new technologies like AI, while also doubling down on fundamentals like quality content, fast and friendly websites, and understanding our audience’s intent.
The competition for organic traffic can be intense, but remember that with every change comes new opportunities.
Today’s emerging trend (for example, optimizing for voice search or appearing in an AI overview) could be tomorrow’s standard practice. By reading this far, you’ve equipped yourself with knowledge of what’s shaping SEO right now, and knowledge is power.
Now it’s time to take action. Which of these trends will you tackle first? Perhaps you’ll start by auditing your site’s Core Web Vitals and making UX improvements. Or maybe you’ll experiment with an AI tool to speed up content creation (while ensuring you add your unique spin).
You might even identify a handful of long-tail keywords from this post and create new content targeting them. Whatever it is, commit to implementing at least a few improvements in your SEO strategy in the coming weeks.
Staying ahead in SEO is a continuous journey of learning and adapting. Keep your finger on the pulse of new developments, be willing to test and iterate, and always center your strategy around providing real value to searchers. If you do that, you won’t just keep up with the SEO trends, you’ll set the pace.
Ready to elevate your SEO game?
Apply these trends and tips to your site and watch your rankings climb. If you found this guide useful, feel free to share it with fellow marketers or drop us a comment with your thoughts. If you want to dive deeper into SEO strategies, check out our detailed technical SEO guide here. Here’s to staying ahead of the curve and conquering the SERPs in 2025!






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)