SEO Techniques: 60+ Strategies to Boost Your Google Rankings
August 12, 2025
Introduction: Why SEO Techniques Matter
Did you know the top 3 Google results capture about 60% of all clicks? If your website isn’t on page one, you’re missing out on a huge share of potential traffic. That’s where mastering SEO techniques comes in.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is defined as the process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic from search engines. In practice, SEO means optimizing your site’s content, structure, and reputation so it appears higher in search results for relevant queries.
Why is this so important?
Because search engines (especially Google) are constantly evolving. What worked a few years ago, stuffing keywords or buying shady links, no longer cuts it. In fact, “the 2015 version of SEO” is dead.
Today, Google’s algorithm values relevance, quality, and usability above all. New technologies like AI-driven search results and voice search are changing how people find information online.
However, one thing remains constant: people still use search engines billions of times per day to answer questions and find solutions. If you optimize your site using modern SEO techniques, you can tap into this huge audience, drive more organic traffic, and grow your business without spending a fortune on ads.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover 60+ actionable SEO techniques to help you dominate the search rankings. From keyword research and on-page tweaks to technical fixes and link-building strategies, we’ll walk through each step with practical tips.
We’ve also included the latest SEO trends for 2025, like adapting to AI in search results and emphasizing E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust).
Whether you’re an SEO beginner or a seasoned pro looking for new ideas, this guide will help you stay ahead of the competition. Let’s dive in and start boosting your Google rankings!
An SEO-optimized website can attract significantly more organic traffic, as effective optimization helps search engines understand and rank your content.
What Is SEO and Why It’s Critical
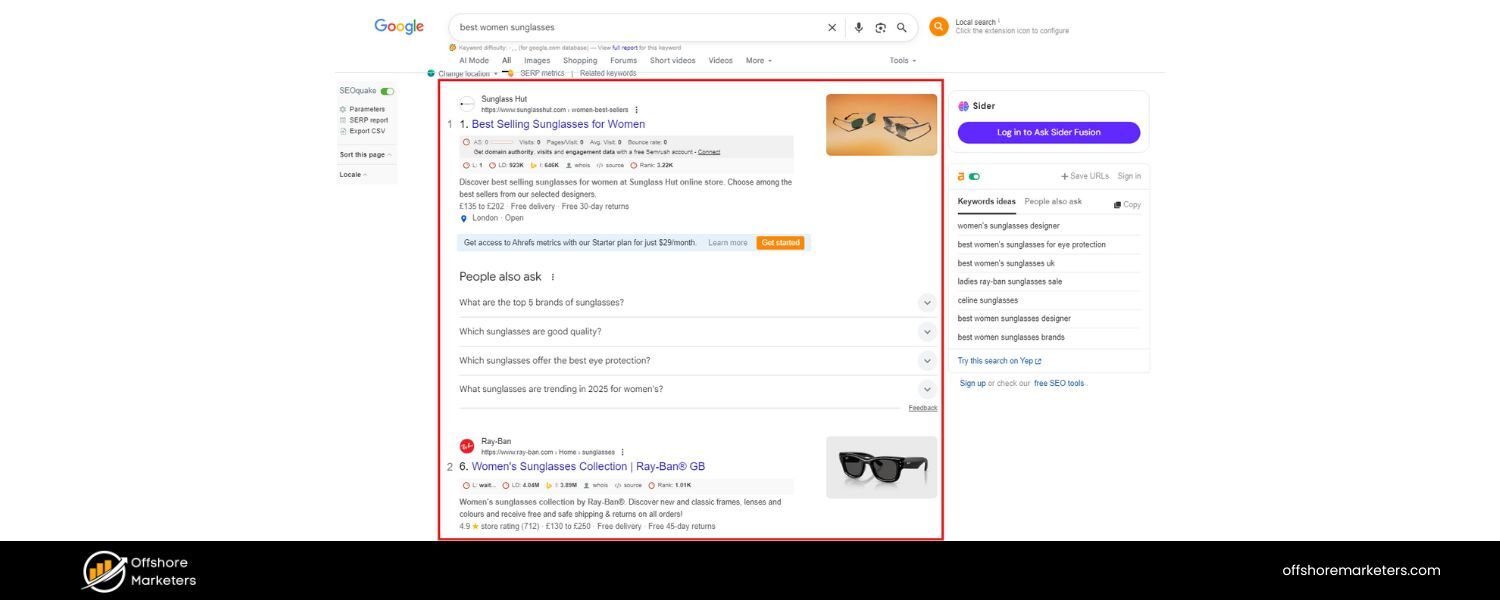
Before jumping into techniques, let’s clarify the fundamentals. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is “the process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website or a web page from search engines”.
Unlike paid advertising, SEO focuses on earning free (organic) traffic by making your site more visible and relevant to people’s searches.
In 2025, SEO is more critical than ever for a few key reasons:
A. Higher Competition
Millions of websites are vying for attention. If you ignore SEO, competitors who optimize their sites will outrank you. Given that the first page of Google captures the vast majority of clicks, you need SEO just to stay visible.
B. Evolving Search Landscape
Search engines have gotten smarter. Google’s algorithms (from RankBrain to the 2024 Helpful Content updates) now prioritize user experience and intent over simple keyword matching. SEO techniques have evolved to focus on quality content, fast and mobile-friendly pages, and authoritative backlinks – all things we’ll cover in this guide.
C. Organic Traffic = Lasting Value
Unlike paid ads that stop when your budget runs out, SEO efforts can generate sustained traffic over time. By investing in solid SEO strategies now, you build a foundation for long-term visibility and brand awareness.
D. Trust and Credibility
Ranking high organically often makes your brand appear more trustworthy to users (compared to an “Ad” label). Good SEO, such as obtaining quality backlinks and positive reviews, also boosts your site’s credibility in the eyes of search engines and consumers.
In short, mastering SEO means aligning your website with what search engines want – which ultimately comes down to what users want. Google’s own SEO starter guide emphasizes creating helpful, people-first content and ensuring a great page experience (fast, mobile-usable, secure).
The following sections break down exactly how to do that, with practical techniques you can start applying today.
1. Keyword Research and Search Intent
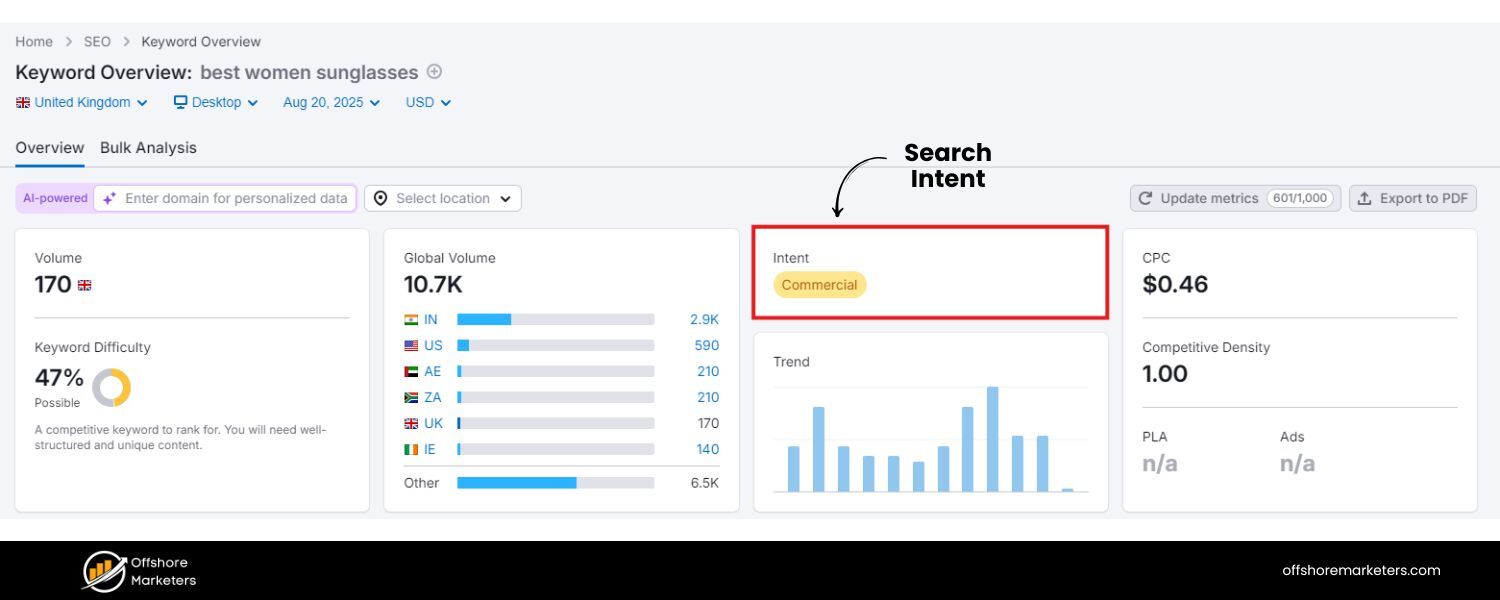
Keywords are the foundation of SEO – they’re the terms people type or speak into search engines. Effective keyword research ensures you’re targeting the phrases your audience actually uses, including valuable long-tail keywords (longer, specific phrases) that often indicate high intent. In 2025, keyword research goes hand-in-hand with understanding search intent – the why behind a query.
How to find the right keywords:
A. Brainstorm Seed Topics
Start with broad topics related to your business. For example, a bakery might start with “artisan bread,” “wedding cakes,” etc. Think about what your ideal customer might search for.
B. Use Keyword Tools
Leverage SEO tools (many have free versions) to expand your list. Google’s own autocomplete suggestions are a great quick source – type a query and note the suggestions that appear (these “Google Suggest” phrases are often valuable long-tails). Dedicated tools like Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool or Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer help find keywords along with data on search volume and difficulty.
C. Explore Online Communities
Platforms like Reddit and Quora are keyword goldmines. Browse subreddits or Q&A threads in your niche to see the wording real people use. Look for recurring questions or problems – if people are asking about it, they’re likely searching for it too.For instance, if many users on a gardening forum ask “how do I get rid of tomato blight?”, that phrase (or its variants) could be a great long-tail keyword for a gardening site.
D. Check Competitor Keywords
See what terms drive traffic to your competitors. SEO tools can show you competitor “top pages” and keywords. If other sites rank for keywords you haven’t covered, consider creating content for those topics (this is called a content gap analysis).
E. Prioritize Strategically
Not all keywords are equal. Especially if your site is new or small, prioritize low-competition keywords that you have a realistic chance to rank for. Look at keyword difficulty scores in tools, and find queries where some lower-authority sites already rank – a sign you could too. Over time, as your site grows, you can target more competitive, high-volume terms.
Understanding search intent is equally important. Every query falls into an intent category: informational (seeking knowledge), commercial (researching products), transactional (ready to buy or take action), or navigational (looking for a specific site). For each keyword you target, shape your content to match the intent.
For example, someone searching “best DSLR cameras 2025” likely wants an informational list of top cameras (so a blog post reviewing top models fits), whereas “buy Nikon D3500 online” is transactional (so an e-commerce product page would be ideal).
Pro Tip
Examine the current top Google results for your target keyword to decipher intent. Are most results blog posts, videos, product pages, or something else? Google is telling you what it believes searchers want. Align your content accordingly.
In one case, an SEO expert found his guide wasn’t ranking well for “increase website traffic” because it was an in-depth tutorial, while the top results were list-style tips.
After he rewrote his content into a list of tactics to better match user intent, the page shot into the top 3 and saw a 70% traffic boost.
Finally, aim to cover keywords comprehensively. This means using related terms and synonyms in your content (often called Semantic SEO). For instance, if your keyword is “digital marketing strategies,” related terms might include “social media marketing,” “SEO tactics,” “content marketing” and so on.
Sprinkle these naturally in your article. This not only helps you rank for more long-tail variations, but also signals to Google that your content is topically relevant. You can find related keywords in Google’s “People also ask” and “Searches related to…” sections, or by using tools like Answer The Public (which visualizes questions people ask).
By investing time up front in keyword research and understanding user intent, you set a clear roadmap for your SEO content strategy. You’ll know what topics to create or optimize, which phrases to target, and how to tailor your pages to give searchers exactly what they’re looking for.
2. On-Page Optimization Techniques
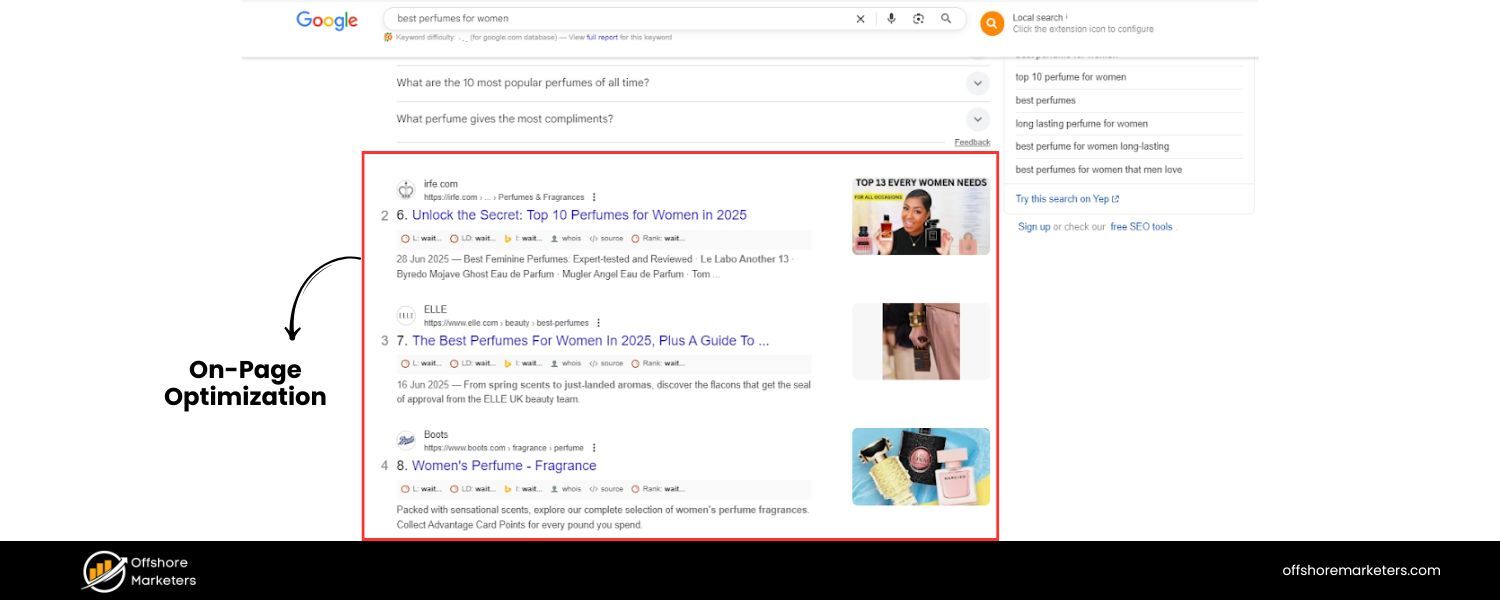
On-page SEO refers to all the measures you can take within your own website’s pages to help them rank higher. It’s about making your content as understandable and enticing as possible – for both search engines and human readers. Here are the core on-page elements to focus on:
A. Title Tags (Page Titles)
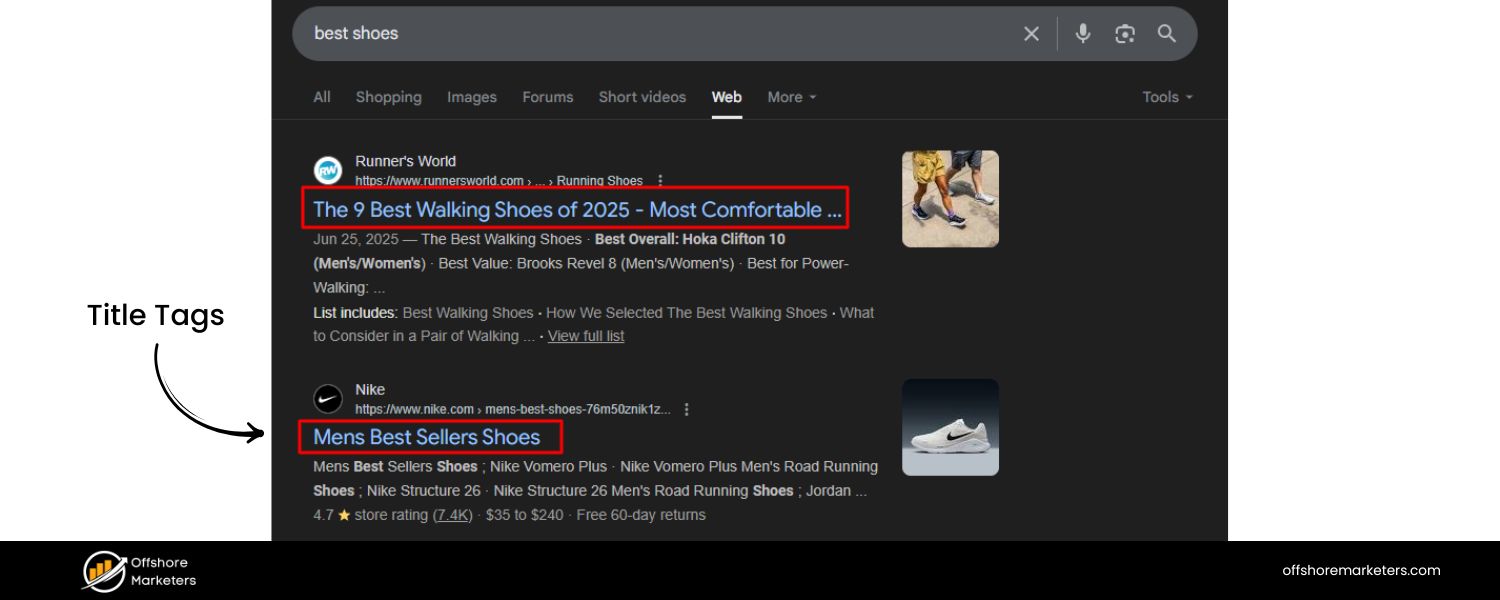
Craft a unique, descriptive title for each page, ideally including your primary keyword. The title tag is usually what shows up as the clickable headline in search results, so it has a huge impact on both ranking and click-through rate.
Keep titles around 50-60 characters so they don’t get cut off, and make them compelling to encourage clicks (e.g. “10 Surprising Benefits of Yoga for Mental Health” is more enticing than “Benefits of Yoga”).
B. Meta Descriptions
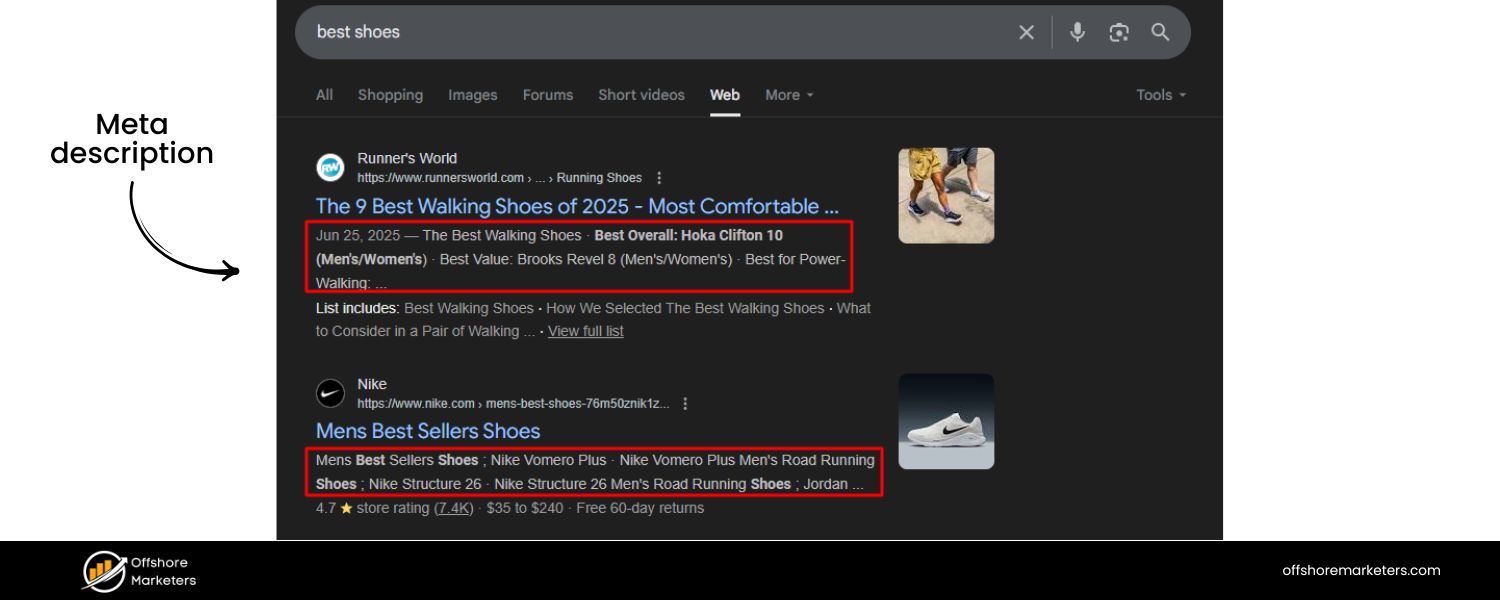
This is the snippet of text under the title in search results. While not a direct ranking factor, a well-written meta description can boost your click-through rate (CTR), which is a positive signal.
Summarize the page in 1-2 sentences, include the target keyword, and use a call-to-action or value proposition to make searchers want to click. For example: “Learn 10 proven yoga benefits backed by science – from stress reduction to better sleep. Find out how yoga can transform your mental health in this in-depth guide.”
C. Headings (H1, H2, H3) 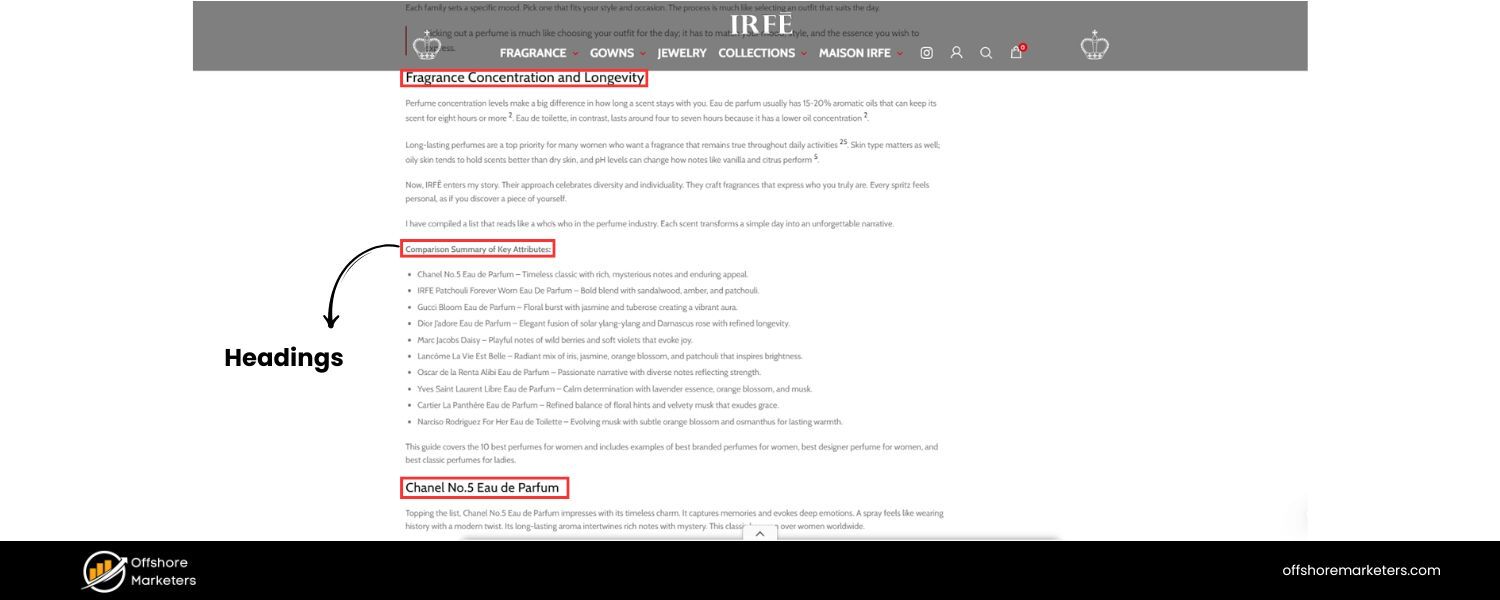
Use heading tags to structure your content hierarchically. The H1 is usually the title of your article (often mirrors the title tag). Use H2s for main subtopics, and H3s for sub-points under those, etc.
This not only makes it easier for readers to skim, but search engines also rely on headings to understand the main topics of your page. Include relevant keywords in some headings naturally, but keep them descriptive of the section’s content.
D. Keyword Placement
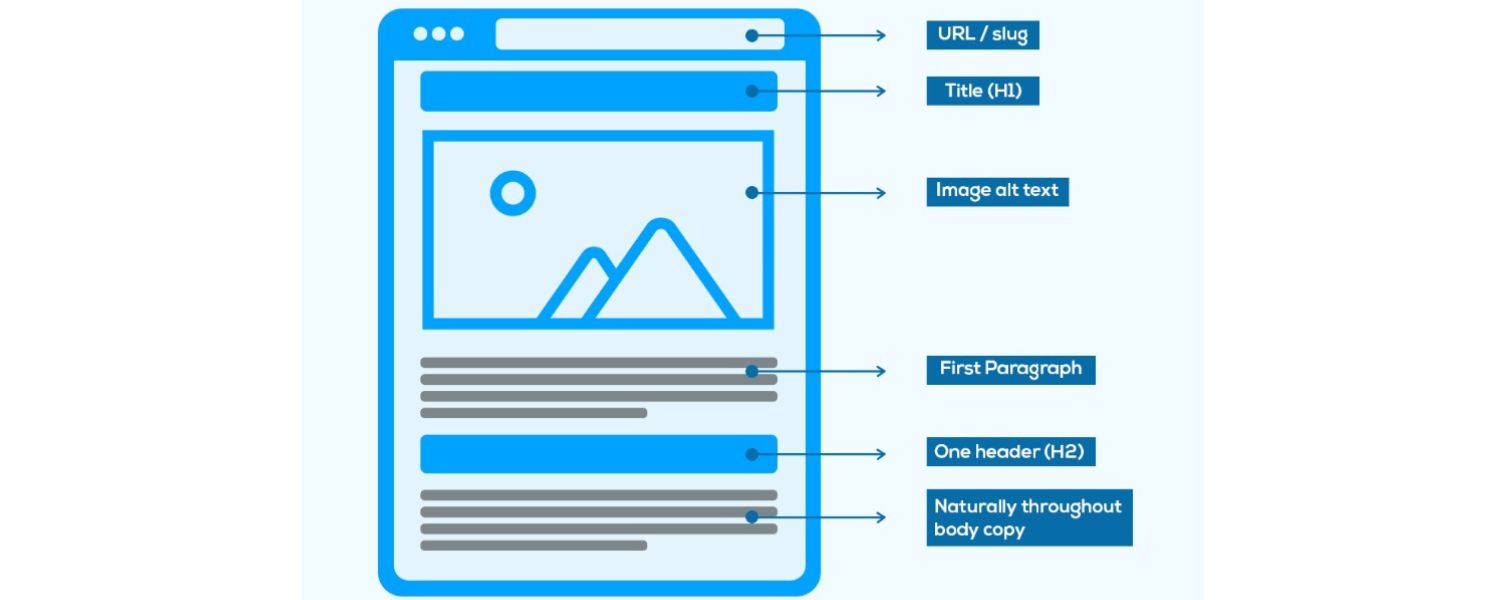
Ensure your primary keyword (and close variants) appear in the important spots: the title, first paragraph, headings (where relevant), and sprinkled throughout the body. But avoid keyword stuffing, don’t force the keyword unnaturally or repeat it too often.
Google is smart enough to detect synonyms, and a page that reads poorly will turn off readers (leading to higher bounce rates, which can hurt rankings). Aim for a natural frequency; a good rule of thumb is if you write comprehensively on a topic, your keywords and related terms will naturally appear.
E. Content Quality and Length
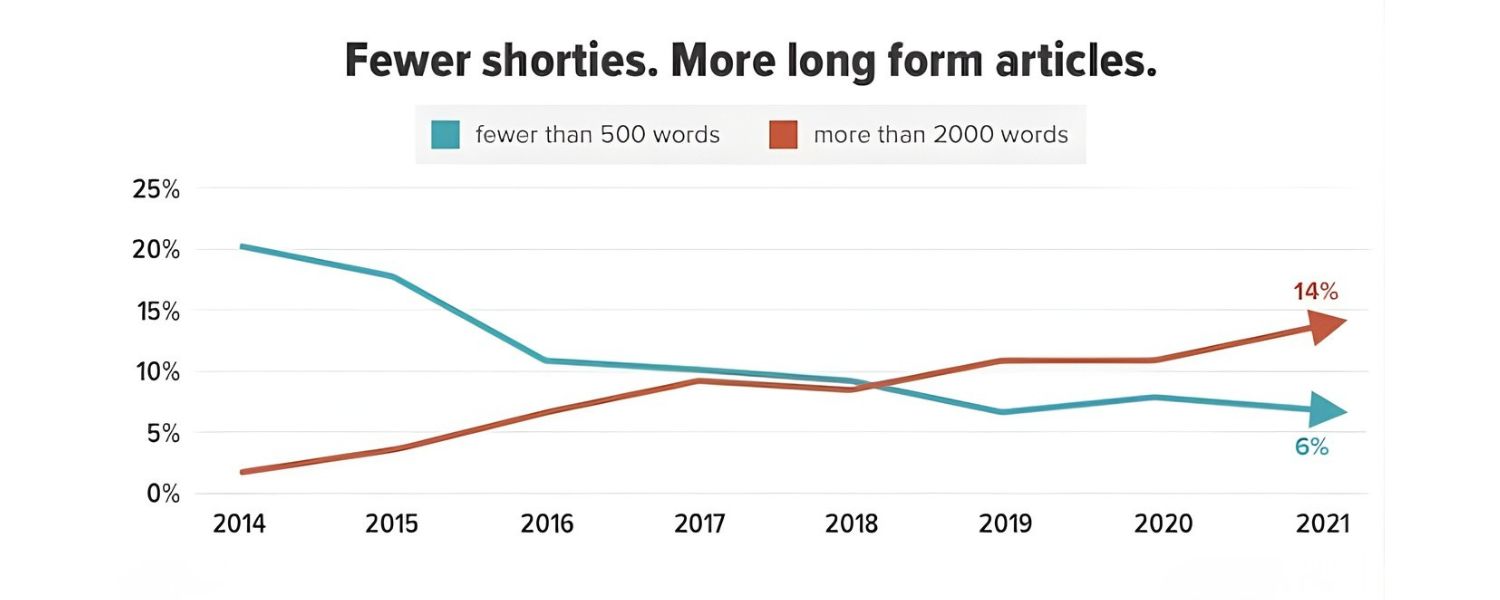
High-quality, relevant content is non-negotiable. Your page should thoroughly answer the user’s query or provide the information promised by its keyword. In-depth content tends to perform better in search because it covers more subtopics and keeps readers engaged longer.
In fact, one study by Backlinko found that the average first-page result on Google contains about 1,447 words.Don’t fixate on word count for its own sake – focus on covering the topic completely.
Use examples, data, and clear explanations. Also, ensure the content is fresh and up-to-date.Content riddled with typos, outdated info, or broken links will not rank well. Regularly update older posts to keep them accurate (more on content maintenance later).
F. Internal Linking

Link to other relevant pages on your site using descriptive anchor text. Internal links help spread link equity around your site and guide both users and search crawlers to your best content.
For example, if you have a high-authority page on “digital marketing 101,” linking from that page to a newer page about “social media tips” can pass on some SEO value and help the new page rank.
A good practice is to link from your strong pages to pages that need a boost. Also, within a blog post, link to other articles or resources on your site that provide additional value. This keeps readers on your site longer (improving engagement metrics) and helps Google discover and index your content more effectively.
G. URL Structure 
Keep URLs short, keyword-rich, and readable. For instance, use yourdomain.com/organic-gardening-tips rather than yourdomain.com/category/12/post?ID=5748.
Descriptive URLs give users and search engines a clue to what the page is about. Plus, shorter URLs tend to rank better. A study of 11.8 million Google search results found a correlation between shorter URLs and higher rankings.
It’s good to include the main keyword in the URL if possible (e.g., …/yoga-benefits if the keyword is “yoga benefits”). Once a URL is set, avoid changing it – if you must, implement proper 301 redirects to the new URL.
Research suggests that shorter, cleaner URLs often correlate with higher Google positions. Keeping your URL structure concise and keyword-focused can give you an extra SEO edge.
H. Image Optimization 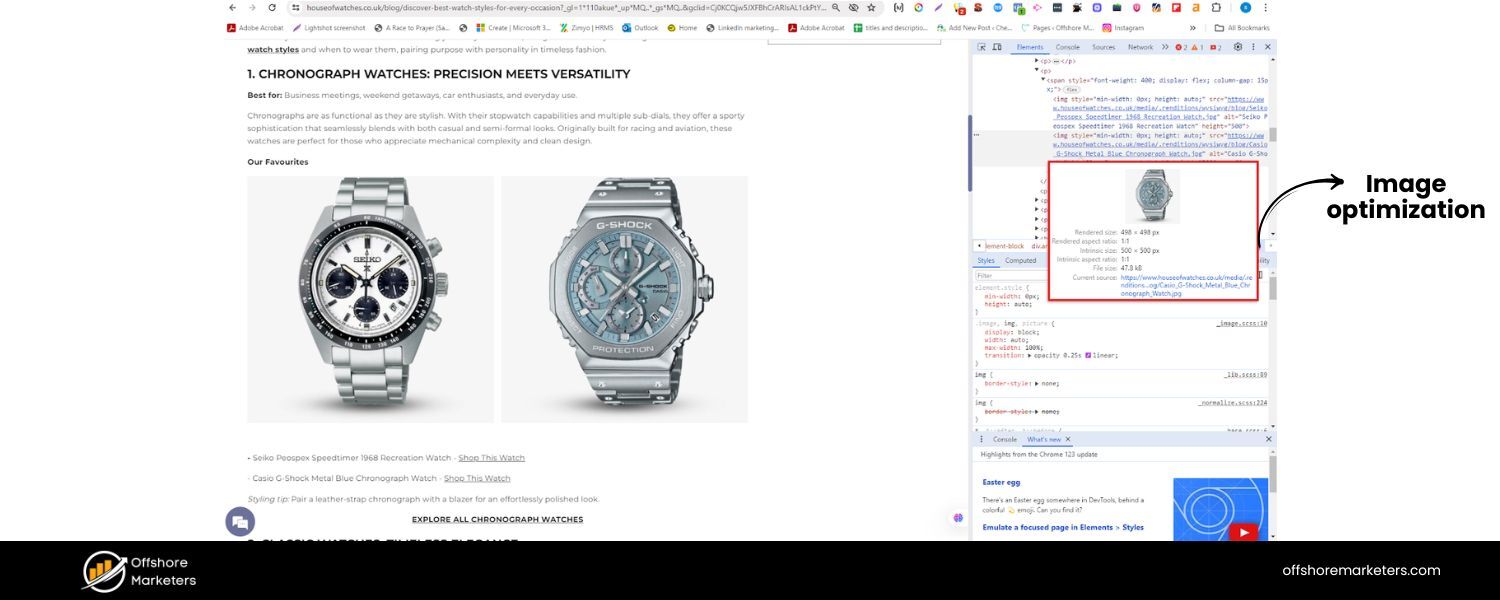
Images can enrich your content, but they should be optimized. Use descriptive file names (e.g., morning-yoga-poses.jpg instead of IMG_1234.jpg) and always fill in the alt text attribute with a brief description of the image. Alt text helps visually impaired users (via screen readers) and gives search engines context about the image.
It’s also an opportunity to include a keyword if relevant. For example, an image of a yoga pose might have alt text like: “Woman doing downward dog pose – yoga for beginners”.
This description both explains the image and naturally includes a keyword.Remember, search engine crawlers can’t “see” images, so alt text is crucial. Additionally, use the right image format and size to ensure fast loading (more on speed in the Technical SEO section).
Compress large images, often you can reduce file size by 50%+ with no visible quality loss.
I. Outbound Links
Don’t be afraid to link out to authoritative sources when it makes sense. Linking to high-quality references (industry studies, official guidelines, etc.) can help support your content and improve user trust.
For example, if you cite a statistic or a definition, linking to the source (like a Google blog or a research paper) is good practice. There is some evidence that linking out to authority sites may slightly help rankings by associating your content with reliable references – at the very least, it makes your content more credible to readers.
Just make sure outbound links open in a new tab (so you don’t completely divert people away) and avoid linking to direct competitors for obvious reasons.
J. Write for Humans First
While it’s important to use keywords and structured data, never lose sight of the human reader. Use a clear, engaging writing style.Break up text with short paragraphs and bullet points (like this list) to improve readability – walls of text can overwhelm readers. Insert relevant images or charts to illustrate points.
If appropriate, use a conversational tone and explain jargon.
The longer you keep visitors engaged and satisfied with your content, the better your SEO will ultimately be (thanks to lower bounce rates, longer dwell time, and higher likelihood of shares or links).
By rigorously applying these on-page techniques, you’re making each page of your site as optimized as possible for its target keywords and topics.
Think of on-page SEO as sending clear signals to search engines about “what this page is about” and “how it serves users.” Combined with the off-page and technical strategies we’ll discuss, solid on-page optimization forms the bedrock of SEO success.
3. Content Strategy and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)

It’s not enough to sprinkle keywords on a page – the overall quality and credibility of your content must be top-notch. Google has increasingly emphasized E-E-A-T in its Quality Rater Guidelines: Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness.
In 2025, demonstrating E-E-A-T in your content is a powerful “technique” in itself to achieve better rankings, especially for topics that impact health, finance, or major life decisions (so-called “Your Money or Your Life” pages). Here’s how to build a strong content strategy with E-E-A-T in mind:
A. Demonstrate First-Hand Experience
Google and users love content that comes from real experience. If you run a tech blog, have actual developers write coding tutorials. If you sell camping gear, include insights from someone who goes camping.
First-hand experience makes your content unique and valuable. Google’s trend is to reward content that isn’t just rehashing what’s already on page 1, but adding new insight.In fact, “Google has called out the need to bake first-hand experience into SEO content”.
This could mean sharing case studies, personal stories, original research, or at least commentary from experts.For example, instead of a generic article on “nutrition tips,” a piece written (or reviewed) by a certified nutritionist who mentions their own client experiences will likely carry more weight.
B. Establish Expertise
Wherever possible, create content (or have it written by people) who are knowledgeable in the subject. Cite credentials or background. For blog posts or articles, consider including an author bio that highlights why that author is an expert in the topic (e.g., “Jane Doe, Certified Personal Trainer with 10 years of experience”).
You can also mention if content was reviewed by a professional (common on medical or legal sites). This signals to readers and Google that the information is reliable.
It’s also wise to cite credible sources within your content to back up facts – linking to academic studies, official statistics, or reputed industry publications adds to the perceived expertise and accuracy of your page.
C. Build Authority
Authority in SEO often comes down to your site’s reputation and backlinks (more on link building in the next section). But from a content perspective, you build authority by covering topics comprehensively over time. Aim to become a go-to resource in your niche.
One strategy is creating content hubs or clusters: a comprehensive “pillar” page on a broad topic, supported by multiple in-depth articles on subtopics (all interlinked).
For instance, you might have a pillar page on “Digital Marketing Strategies” and individual pages on SEO, PPC, Social Media, Email Marketing, etc., all linking back to the pillar. This signals topical authority to Google.
Additionally, encourage satisfied readers to share and link to your content – the more your content is referenced by others, the more authoritative it appears.
D. Foster Trustworthiness
Trust is built through accuracy, transparency, and user signals. Ensure your content is fact-checked and up-to-date. Correct any inaccuracies and update statistics to the current year. If your site deals with product reviews or money matters, be honest and disclose affiliations or biases.
Having a clear contact page, privacy policy, and terms of service also contribute to site trust. From an SEO perspective, user reviews and reputation matter too – a positive online reputation (whether via Google reviews for a local business, or just mentions on forums/social media) can indirectly boost your SEO.
Google’s quality guidelines note that positive user feedback and the absence of negative sentiment contribute to a site’s trustworthiness. Monitor what people say about your brand and address complaints if any (this can also fall under online PR, which intersects with SEO).
E. Use Multimedia & Visual Aids
High-quality content isn’t just text. Enhance your pages with relevant images, videos, infographics, or charts. This improves user engagement (people spend more time on pages with visuals) and can improve your chances of ranking in image search or getting rich results.
For example, incorporating a helpful video and its transcript on a tutorial page can cover both traditional search and those who prefer visual learning.As an added SEO bonus, images and videos can sometimes earn you traffic through Google Images or Video carousels.
Just remember to optimize media (alt text for images, and proper titles/descriptions for videos).As noted earlier, ensure multimedia elements are properly compressed/formatted so they don’t slow down the page.
F. Answer Common Questions & Aim for Snippets
Part of a good content strategy is anticipating what questions users will have and directly answering them.This not only improves user satisfaction but also positions your content to capture featured snippets (the quick answer boxes on Google).
For instance, in an article about planting tomatoes, you might have an H2 like “How much sun do tomato plants need?” and then a concise answer.
Structuring some content in Q&A or concise definition format can help you get those coveted snippet spots, which often appear above regular results.
Moreover, consider adding an FAQ section at the end of key pages addressing related queries – you can even use FAQ schema markup (structured data) to potentially get rich snippet treatment in the SERPs.
G. Regularly Audit and Update Content
The work isn’t done once you publish. Make it a habit to review older content periodically. Update outdated information, improve titles/meta descriptions, and add new sections if needed (especially if the topic has had new developments).
Pages can lose ranking over time as they grow stale – a refresh can often reclaim lost positions. Also fix any broken links or images when you find them (use tools or Google Search Console to spot these).Updating content sends a freshness signal to search engines and shows readers that you’re providing current info. For example, if you have a “Best Smartphones 2023” post, update it to “2025” with the latest models – you might even redirect the old URL or create a new one, depending on your strategy.
Many top sites will republish updated content with a current date to improve rankings (Google tends to favor fresher content for queries where currency matters).
Remember, at the heart of all this is providing genuine value. Google’s algorithm is essentially trying to reward content that is helpful, relevant, and satisfying to users. If you focus on that mission – and use the techniques above to signal your content’s quality – you’ll not only rank better, but also earn the trust and loyalty of your audience.
Brands that establish themselves as authoritative and trustworthy in their field will have a competitive SEO advantage moving forward.
Lastly, don’t shy away from leveraging user-generated content and feedback as part of your content strategy. Encouraging comments on blog posts, engaging with your community on forums or social media, and even featuring user testimonials can enhance E-E-A-T.
A lively comment section with thoughtful discussion can demonstrate that your content inspires engagement (just moderate out spam). If people ask questions in comments, answer them – this can further enrich the content on the page (which search engines notice).
In summary, prioritize content quality over quantity. A single superb, authoritative article can outperform 10 mediocre ones. Marry your SEO tactics with editorial excellence. That’s the formula for sustained success in the era of E-E-A-T.
4. Technical SEO Techniques (Site Performance & Indexability)
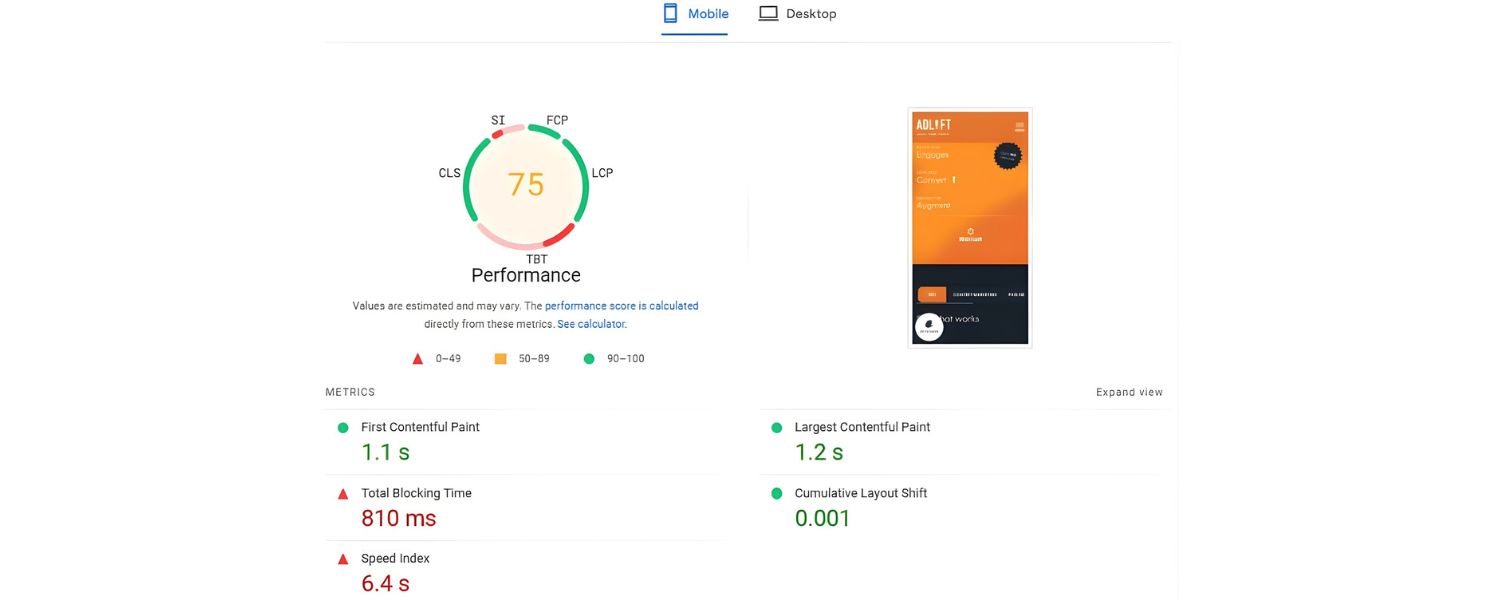
Even the best content won’t rank if search engines can’t properly crawl and index your site, or if your user experience is poor. Technical SEO covers the behind-the-scenes optimizations that make your site fast, accessible, and understandable to search engine bots. Here are the key technical techniques to implement:
A. Boost Site Speed 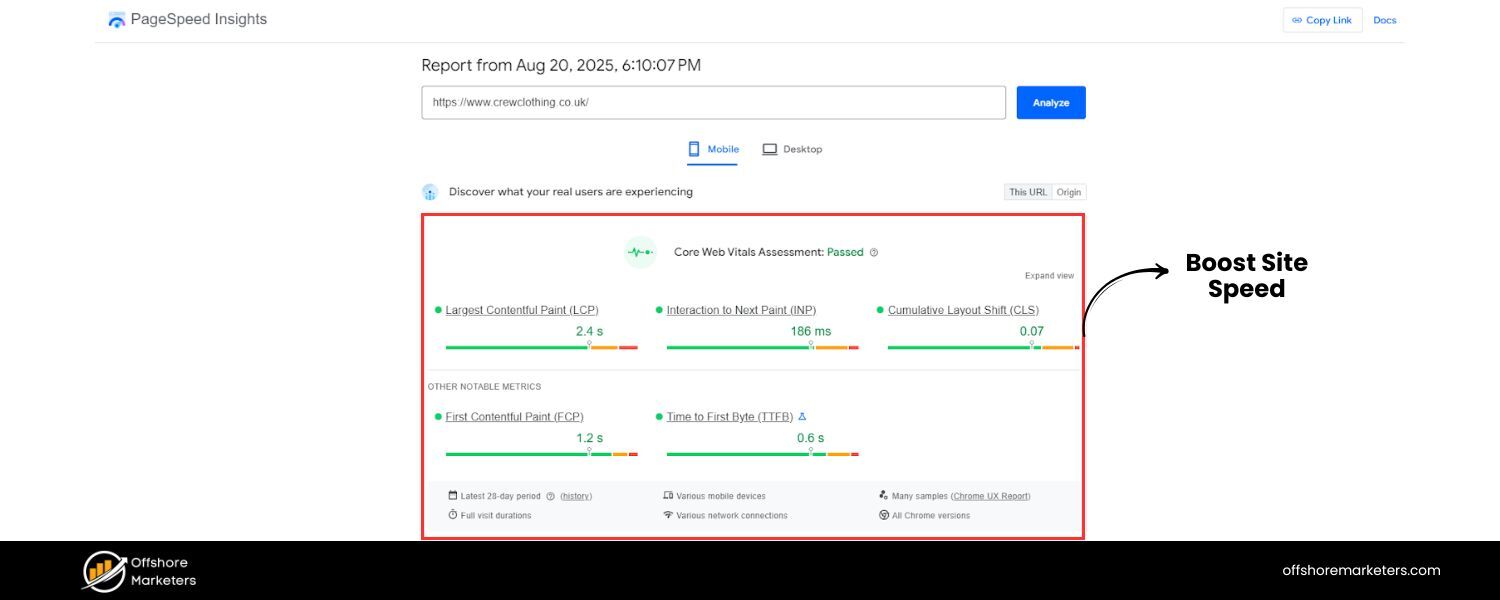
Website speed is crucial – both for user experience and SEO rankings. Google’s Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, Cumulative Layout Shift) are specific page speed and stability metrics that influence rankings. To improve speed:
1. Enable Caching
Use a cache plugin or server-side caching to serve static versions of pages, reducing server processing on repeat visits. For WordPress, plugins like WP Rocket or WP Super Cache can yield significant speed gains.
2. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your content across global servers, so users fetch data from a location closer to them. This can drastically cut load times for worldwide visitors. Many CDNs (Cloudflare, Fastly, etc.) also optimize file delivery and provide security benefits.
3. Optimize Images and Media
Compress images (as mentioned in On-Page tips) – tools like TinyPNG or image optimization plugins can automate this. Serve images in modern formats like WebP if possible (smaller file sizes). Also, implement lazy loading for images and videos, so they only load when a user scrolls to them, rather than all at once.
4. Minify and Combine Files
Minify your CSS, JS, and HTML files (remove unnecessary whitespace/comments) to reduce file size. Also combine files if you have many small ones, to reduce HTTP requests. Most performance plugins handle this, or you can use build tools for the same.
5. Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources
Ensure that important content isn’t delayed by bulky scripts. If you have JavaScript that isn’t needed upfront, load it asynchronously or defer it. Similarly, use inline critical CSS for above-the-fold content.
6. Monitor Speed
Regularly test your pages with tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. They provide specific recommendations and show which elements are slowing you down. Aim for a mobile PageSpeed score in the green (90+ if possible), as mobile performance is especially important with Google’s mobile-first indexing.
7. Mobile-Friendliness
By now, mobile-first indexing means Google predominantly uses the mobile version of your site for ranking and indexing. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, it will severely hurt your rankings on mobile searches (and possibly desktop too, since indexing is mobile-first). Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool – you want the result to say “Page is mobile-friendly.”
If it’s not: Ensure your site uses responsive design (preferred) or a dynamic serving mobile version. Content should adapt to smaller screens; no horizontal scrolling or tiny tap targets. Avoid software not common on phones (Flash, etc.). Use modern, mobile-compatible tech.
8. Optimize for mobile UX
adequate font sizes, button sizes, and easy navigation. Pop-ups or interstitials that cover content on mobile are a big no-no (Google may penalize pages with intrusive interstitials).Check Core Web Vitals on mobile specifically, sometimes a site is fast on desktop but slow on a phone due to different resources loading.
If you run an online store or similar, test the checkout or form processes on mobile thoroughly. Any key functionality that breaks on mobile will also break your SEO in a sense (users will bounce, and Google might pick up on it).
9. XML Sitemap
Create and maintain an XML sitemap listing all important pages on your site. This sitemap acts like a roadmap to ensure search engine crawlers can find and index your content. For most CMS platforms, there are plugins or built-in features to generate sitemaps (e.g., Yoast SEO or RankMath for WordPress).
Once you have a sitemap (usually at yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml), submit it in Google Search Console for good measure. An XML sitemap is especially helpful for new sites or if you have a large site with deep pages – it ensures nothing gets overlooked during crawls.
10. Robots.txt and Crawl Management
Your site’s robots.txt file tells crawlers which pages or sections to avoid. Make sure you’re not inadvertently blocking important pages. A common mistake is disallowing whole directories (or leaving a development block in place) that prevent Google from crawling your site. You can check robots.txt by going
to yourdomain.com/robots.txt.Generally, allow everything except possibly admin or login pages. If unsure, a minimal robots.txt that allows all (or none at all, since by default Google will crawl anything it can find) is better than an overly strict one. Also, avoid using noindex on pages that should rank.
It sounds obvious, but sometimes sites accidentally tag sections as noindex (like category pages or even entire blogs). Use Google Search Console coverage report to see if pages are being excluded due to noindex or robots directives.
11. Structured Data & Schema Markup
Adding schema markup to your pages can enhance how your listings appear in search results (though it doesn’t directly boost rankings, it can indirectly improve CTR).For example, you can add FAQ schema to Q&A content, recipe schema to recipes (showing ratings, cook time, etc.), product schema for e-commerce (showing price and stock), and so on. Rich results stand out and can increase clicks.
To implement, you can use JSON-LD scripts in your HTML or plugins if you’re on a CMS. Google has a Structured Data Testing Tool (now incorporated in Rich Results Test) to validate your markup. Focus on schema that is relevant to your content and supported by Google.
Even something as simple as BreadcrumbList schema can display breadcrumb navigation in your result, which is good for CTR. Using schema shows search engines the specific properties of your content (like defining what’s the author, the published date, an image, etc.), which can only help them interpret your pages better.
12. Fix Crawl Errors & Broken Links
Regularly check Google Search Console for crawl errors. If Google encounters 404s (page not found) or other errors on your site, fix them. This might involve 301 redirecting broken URLs to the appropriate new URL or to a relevant page.
It’s also good to scan your site for broken outbound links – those don’t directly harm SEO much, but they hurt user experience. Internally, definitely fix broken links or mis-linked URLs (they waste crawl budget and frustrate users).
There are free tools and crawlers (like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or some online services) that can scan for broken links. A thorough site audit can uncover technical issues like duplicate content, missing meta tags, broken links, or slow pages.
Addressing these issues will improve your site’s overall SEO health. As one example, cleaning up a bunch of 404 errors (by redirecting them properly) can help ensure any residual link equity is preserved and that users don’t hit dead ends.
13. HTTPS and Site Security
This might be old news, but if your site somehow still isn’t on HTTPS, make the switch. Google has used HTTPS as a lightweight ranking signal for years, and browsers will warn users that your site is “not secure” if it’s not HTTPS, which can tank your credibility.
Get an SSL certificate (many hosts offer free Let’s Encrypt certs) and redirect all HTTP pages to HTTPS. Beyond that, ensure your site doesn’t have security issues – sites that get flagged for malware or phishing are dropped from search results until cleaned.
Use Google Search Console’s Security Issues report to monitor, and keep your software/plugins up to date to prevent hacks.
14. Canonicalization
If you have multiple URLs with identical or very similar content (like print versions of pages, or HTTP vs HTTPS duplicates, or tracking parameter variants), use the canonical tag to indicate the primary version.
For example, in the of duplicate pages tells Google that the given URL is the canonical one to index. This prevents duplicate content issues and consolidates ranking signals to the main page.
Also, be consistent with your internal linking, always link to the canonical version of a URL. This technical detail helps avoid splitting your SEO power across duplicates.
15. Pagination and Indexing Controls
If you run an e-commerce site or any site with pagination (page 1, 2, 3 etc. for categories or articles), ensure you handle those correctly. Google now usually figures out how to handle paginated series, but you can use rel=“next” and rel=“prev” in the HTML of paginated pages as hints.
Additionally, for any content you don’t want indexed (like internal search result pages, or certain thin pages), use noindex meta tag rather than robots.txt disallow (if they’re accessible).
Noindex will let Google crawl but not index, which is fine; disallow prevents crawling entirely – if Google finds links to those pages, it might still index the URL without content, which isn’t ideal.
16. Use Search Console & Analytics Data
Google Search Console is a goldmine for technical insights. It will alert you to coverage issues, mobile usability problems, Core Web Vitals reports (showing what percent of your pages have good LCP, etc.), and even security issues or manual penalties.
Check it monthly at least. Likewise, Google Analytics (or any analytics) can show if certain pages have unusually high bounce rates or very low time-on-page – that could indicate a technical or content relevance issue worth investigating.
By making your site technically sound, fast, crawlable, and free of errors, you create a solid foundation for all your other SEO efforts to shine.
Think of technical SEO as ensuring that nothing is holding your site back. You don’t necessarily get “bonus points” for perfect technical SEO, but you will be penalized (directly or indirectly) if you have glaring issues.
Many technical fixes are one-time (or occasional) tasks that yield ongoing benefits. So, it’s well worth the time investment to audit your site and implement these improvements.
5. Link Building and Off-Page SEO Techniques
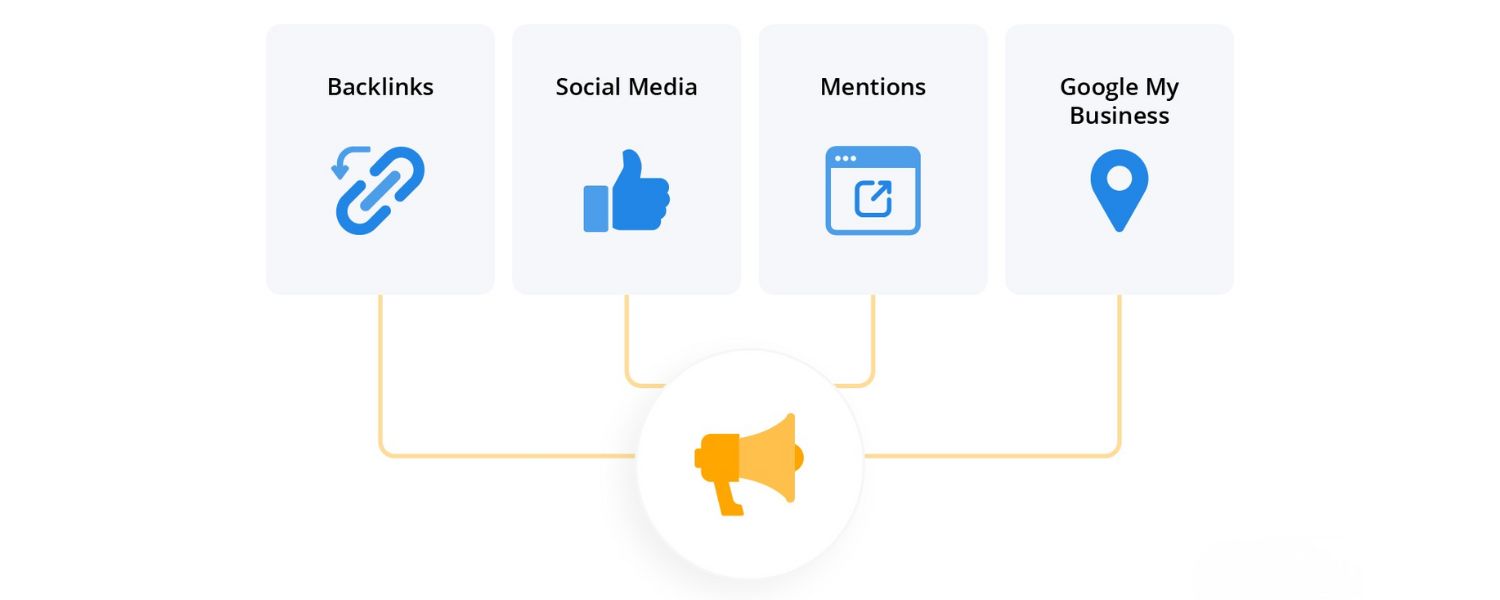
While on-page and technical SEO get your site in great shape, off-page SEO, particularly backlink building, is what often propels a site to the top of Google. Backlinks (links from other websites pointing to yours) remain one of Google’s most influential ranking factors.
The logic: if many quality sites “vote” for your content by linking to it, it must be authoritative or useful. However, not all links are equal, and how you earn them matters. Here are effective off-page SEO techniques for 2025:
A. Create Link-Worthy Content
The cornerstone of earning backlinks is having content others want to link to. This is often called “link bait,” but in a good way. Think infographics, comprehensive guides, original research/data, handy tools/calculators, or even controversial/opinion pieces that spark discussion.
One effective strategy is to curate industry statistics or insights into one resource – e.g., “Social Media Marketing Statistics 2025: 50 Stats You Need to Know.” Such posts naturally attract backlinks because other writers will cite your compiled stats in their articles.
Another example: run a unique study or survey in your niche and publish the results (even a small-scale study can get cited a lot if the data point is interesting). Content that evokes emotion or solves a common pain point tends to earn shares and links. Before you reach out asking for links, make sure you have something link-worthy on your site.
B. Guest Blogging and Contributing
One tried-and-true method is guest posting on other reputable blogs in your industry. You provide a quality article for their blog, and in return you usually get an author bio link or can contextually mention your site.
The key here is to target reputable sites (avoid spammy “write for us” farms) and to actually contribute valuable content – never spin articles or use the same piece on multiple sites.For instance, if you are an expert in finance, writing a guest column on a well-known finance site can net you a strong backlink and also build your reputation.
As the Solvid guide suggests, start by making a list of sites in your niche and pitching them content ideas that would genuinely benefit their readers. Over time, even a handful of high-quality guest posts can significantly boost your backlink profile.
C. Broken Link Building
This tactic involves finding broken links (404 errors) on other websites, and suggesting your content as a replacement if it fits.For example, if you discover that a popular blog has a broken link to an article about “email marketing tips” (perhaps the page was removed), and you happen to have a great article on that topic, you can reach out to the webmaster politely: inform them of the dead link and recommend your live link as an alternative.
Many site owners appreciate being notified of broken links and will swap in your link if your content is a good match. This requires some research – using tools or extensions to find broken links on sites, or searching for keywords + “404 not found” and such. It’s a bit of a numbers game but can yield excellent contextual links.
D. “Skyscraper” Content and Outreach
Coined by Brian Dean, the Skyscraper Technique means finding content that has lots of links, creating something even better, and then reaching out to those who linked to the original to link to yours instead.
For instance, if there’s a “50 SEO Tips” article from 2018 with many backlinks, you could create a fresh “100 SEO Tips for 2025” post that’s more comprehensive and up-to-date. Then you’d contact sites that linked to the old article, letting them know about your new resource.
Not everyone will switch, but some might, especially if the old content is outdated or the link is broken. This method leverages existing link opportunities by offering a superior piece of content.
E. Build Relationships and Networking
A lot of link building comes down to relationship building. Engage with influencers and bloggers in your niche on social media, comment thoughtfully on their posts, share their content, and generally get on their radar before asking for anything. Often, backlinks come naturally when you’re in the right circles.
You might collaborate on a project, join a podcast, or co-author a piece – which can all lead to links. Online communities (forums, Slack groups, LinkedIn groups) related to your industry are also places to be active.
Just don’t be the person who joins and immediately starts dropping links – contribute genuinely. Over time, as people recognize your expertise, they may reference or cite your work without you even asking.
F. Leverage PR and Brand Mentions
Public Relations (PR) can be a powerful way to earn high-authority links. This can include getting mentioned in news articles, interviews, or roundups. Tools like HARO (Help A Reporter Out) connect journalists with sources – responding to HARO queries with expert insights can land you quotes in publications (with a backlink to your site as attribution).
Also, monitor your brand mentions across the web. If someone mentions your brand or content but doesn’t link, politely reach out and ask if they wouldn’t mind turning the mention into a link. If you have images or infographics that others use, you can request attribution links as well.
Essentially, convert unlinked mentions into links. Many site owners will oblige if your content was the source.
G. Participate in Q&A and Forums (Carefully)
Platforms like Quora, Stack Exchange, Reddit, or niche forums can get your content in front of a relevant audience. If someone asks a question that one of your blog posts perfectly answers, you can respond with a helpful summary and link to your post for more detail.
Solvid’s guide notes that answering Quora questions thoughtfully can drive a stream of backlinks, as others might stumble upon your answer and link to your site in their articles.Caution: Always add value in your answers; if you just spam links, you’ll be ignored or banned.
But a well-crafted answer that just happens to reference your own article (among other helpful info) can earn you traffic and sometimes links. Additionally, being active in communities increases your profile.
For example, if you consistently give great answers on a technical forum, bloggers in that space may start citing your blog as an authoritative source.
H. Testimonials and Reviews
Consider writing testimonials for products or services you use. Companies often showcase customer testimonials on their site, sometimes with a backlink.If there’s a tool or service relevant to your industry that you can honestly endorse, see if they accept testimonials – you might get a link on a high-authority site’s testimonials page.
Similarly, if you partner with other businesses, maybe they’ll list you on a partners or clients page with a link. These are usually branded links (like your company name), but that’s fine for diversification.
I. Avoid Spammy Practices
It’s worth mentioning what not to do in link building. Buying links outright is against Google’s guidelines and can result in penalties if caught. Likewise, participating in link schemes (excessive link exchanges, PBNs, or spammy directory submissions) can do more harm than good.
Google’s algorithms, including Penguin and its successors, are very adept at filtering out manipulative links. It’s better to have fewer high-quality links than a bunch of low-quality ones.
If you inherited a site with lots of spammy backlinks, consider using Google’s Disavow Tool for links that appear toxic (though use caution – disavow is a last resort).
J. Quality Over Quantity
One link from a trusted, relevant site can often outweigh 100 links from random low-tier sites. Aim for links that come from domains with solid authority (you can check metrics like Domain Rating or Domain Authority as a proxy) and, importantly, from content that’s contextually related to yours.
A link from a high-quality article about your topic is golden. For example, a link from Wired. com in a tech article to your tech startup carries a lot of weight, whereas a link from a hobby blog sidebar roll might be negligible.
Additionally, diverse link sources (news sites, blogs, forums, etc.) with natural anchor text (not every link saying “best SEO techniques” but some just your brand name or URL) indicate an organic link profile. That’s what you should strive to build.
Off-page SEO can be time-consuming – it often involves outreach that might get ignored or rejected. Don’t be discouraged by low response rates; persistence is key. Personalize your outreach emails (nobody likes a generic template). Highlight the value your content provides.
Over time, as your content library and reputation grow, you may find that links start coming to you without as much active effort – that’s the flywheel effect of great content and smart promotion.
One more tip:
social media can amplify your link-building efforts. While social links themselves aren’t direct ranking boosters, a strong social presence can get your content in front of people who might link to it. For instance, a popular tweet or LinkedIn post sharing your latest blog could attract a journalist or blogger who then cites you.
So share your content across platforms, engage with your followers, and make it easy for people to share (having social share buttons on your content, etc.). The more visibility your content gets, the higher the chance of organically earning links.
In summary, off-page SEO is about building your site’s reputation in the eyes of the web. When dozens of reputable websites are pointing to yours, Google takes notice and will likely reward you with higher rankings.
Combine great content with proactive promotion and relationship-building, and you’ll steadily grow a backlink profile that competitors will envy.
6. Emerging SEO Trends in 2025 (AI, Voice Search, and Beyond)
SEO is never static – staying ahead means adapting to new trends and technologies. As we move through 2025, a few key trends are shaping how we approach optimization. By incorporating these into your strategy, you can steal a march on competitors and future-proof your SEO.
A. AI-Powered Search Results
Perhaps the biggest shift is the rise of AI in search. Google has rolled out its Generative AI Search Overviews (often called SGE – Search Generative Experience) in many results, which use AI to answer queries directly on the results page.
Additionally, Bing integrates GPT-4 in its search. These AI answers can result in more zero-click searches (where users get their answer without clicking any result). However, they also present new opportunities: Google’s AI overviews cite sources, often pulling from sites not necessarily in the top 3 traditional results.
This means even if you’re ranking, say, #8 for a query, you might still get featured as a source in the AI summary if your content directly and succinctly answers the question.
What to do
Continue to produce excellent, authoritative content that answers specific questions clearly.Use FAQ sections, definitions, and step-by-step explanations that an AI might find useful to quote. Also, keep an eye on Google’s moves, for example, if they start highlighting certain types of content (how-tos, definitions, etc.) in AI snippets, tailor some content in that direction.
The good news
Google’s AI has been including more citations, so quality content creators still get traffic. In short, focus on E-E-A-T even more – AI will likely favor content that sounds authoritative and trustworthy.
B. Voice Search Optimization
Voice search continues to grow with the proliferation of Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, etc. In 2025, over 20% of people worldwide use voice search regularly, and that number keeps rising.
Voice queries are usually longer and phrased more conversationally (e.g., “what are the best SEO techniques to improve Google ranking?” spoken vs. “SEO techniques improve ranking” typed).
To capture voice search traffic
1. Target long-tail, conversational keywords and question phrases. Including FAQs in your content, as mentioned, is helpful, voice assistants often pull answers from pages that directly address a specific question.
2. Aim to appear in featured snippets, because many voice assistants read out the featured snippet as the answer.
3. Make sure your site is mobile-friendly and loads fast, since most voice searches happen on mobile devices.
4. Optimize for local voice search if relevant. Many voice searches are local (e.g., “Where’s the nearest coffee shop?”). Ensure your Google Business Profile is up-to-date for local queries.
5. Provide clear and concise answers early in your content when possible. For instance, start a paragraph with a direct answer to a common question, then elaborate. That direct answer might be what the voice assistant uses.
C. User Experience & Core Updates
Google’s algorithm updates increasingly target user experience and content quality. We saw the Page Experience update (Core Web Vitals) and the Helpful Content update in recent years, and this trend will continue.“The shift to user-centric SEO” is basically Google aligning ranking factors with what pleases users.
That means beyond just Core Web Vitals and mobile usability, things like how well your content satisfies the query (dwell time, pogo-sticking rates) could be factored in. Ensure your content gets to the point and delivers value quickly. Organize pages so users can find what they need (for example, use a table of contents for long articles).
Also, consider content design, a well-designed page with visuals, bullet points, and clear typography can keep users engaged longer than a bland wall of text. Google might not “see” design in the traditional sense, but user behavior (which design influences) can indirectly impact SEO.
D. First-Party Data and Privacy
With tighter privacy regulations and changes like the phasing out of third-party cookies, marketers are focusing on first-party data (like email lists, user preferences collected directly) for personalization.
While not an “SEO technique” per se, consider how you can personalize or adapt content to user needs, which leads to higher engagement and return visits. For example, if users can create profiles or wishlists, or if you tailor content recommendations on your blog to what they’ve read before, you could increase user loyalty (and perhaps get more direct traffic, brand searches, etc., which do help your overall SEO presence).
E. Integrated Search Presence
The lines between different types of search results are blurring. It’s not just ten blue links anymore. We have map packs, image carousels, video results, “People Also Ask” boxes, and more.
F. To maximize your search real estate
If relevant, optimize for the local pack: ensure NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency across directories, get Google reviews, and add local schema to your site. A strong local SEO strategy can get you in the map pack for local queries (which often appear above organic results).
G. Video SEO
If you can create video content, do it. YouTube is the world’s second largest search engine, and Google often features YouTube videos for queries (sometimes with key moments highlighted).
Optimize videos with descriptive titles, tags, and engaging thumbnails. Consider embedding videos on your site to enrich content (with proper schema like VideoObject).
H. Image Search
For some industries (fashion, travel, food), image search can’t be ignored. Optimize your images’ alt text and file names as mentioned. Use image schema if applicable. And consider publishing content on image-centric platforms (Pinterest, for example) to draw traffic back to your site.
I. Featured Snippets & Rich Results
We’ve talked about snippets, but also try to win other rich results. For example, if you have a how-to article, use HowTo schema – you might get a rich result with the steps listed out.Google’s Visual Elements Gallery (in their documentation) shows all the types of result features, see which apply to your content and optimize for them.
J. Maintain Ethical SEO Practices
This “trend” is ongoing, but worth reinforcing: Google’s updates increasingly penalize black-hat SEO techniques. In 2024-2025, we’ve seen crackdowns on AI-generated content farms, link spam networks, and manipulative behavior.
For instance, sites pumping out tons of AI-written articles with no oversight have dropped after the Helpful Content updates. If you use AI tools to assist in writing (which is fine), ensure there’s a human in the loop editing and adding originality, quality control is key.
Always optimize for people first, search engines second. If some “hack” seems too good to be true (like a loophole to rank quickly), it probably won’t last long. Focus on sustainable strategies that build real value.
K. Content Refreshes and Updates
We mentioned updating content in the content strategy section, but as a trend: more websites are treating content as evergreen and updatable. Instead of churning out endless new posts, smart SEOs are regularly updating top performers to keep them fresh (and indicating the fresh date).
Google likes fresh content for many queries, and users appreciate when an article has a “Updated Jan 2025” label showing it’s current. So allocate time in your content calendar not just for new creation, but also for refreshing and expanding existing pieces.
L. Holistic Digital Marketing Synergy
SEO doesn’t exist in a vacuum. In 2025, the best results often come from integrating SEO with content marketing, social media, and even paid campaigns. For example, a coordinated approach might be: publish an SEO-optimized blog post, promote it via social and email newsletter to drive initial traffic (which could lead to user engagement signals and even some links if it gets shared widely), maybe run a small ad campaign to get it visibility, and then the increased buzz helps its SEO.
Also, brand building is huge – the more people search for your brand or website directly, the better your organic presence (Google tends to reward strong brands with site links and better rankings).
So, building your brand through PR, social influence, or even offline marketing can positively impact SEO in the long run. It’s hard to measure, but anecdotally, brands that become known entities often see their content rank easier. This ties back to E-A-T as well, Authority and Trust often come with brand recognition.
Staying on top of SEO trends means continuous learning. Make it a habit to follow reliable SEO news sources (Search Engine Land, Moz blog, Google’s own Search Central blog, etc.).
Algorithm changes or new features can emerge with little notice, and adapting quickly can be a competitive advantage. But also, don’t chase every shiny object – evaluate which trends apply to your site.
For instance, if you run a recipe blog, voice search and schema might be important, whereas if you’re B2B SaaS, maybe focusing on long-form content and LinkedIn promotion is more relevant than, say, Pinterest.
To summarize this section
embrace change. SEO in 2025 is far from the simple keyword games of a decade ago. It’s multifaceted, involving technical excellence, content depth, user experience, and an awareness of how emerging tools like AI are changing search behavior.
By keeping these trends in mind and experimenting with new tactics, you can keep your SEO strategy fresh and effective. The only constant in SEO is that it’s always evolving – but that’s what makes it exciting!
Conclusion: Putting It All Together for SEO Success
Congratulations, you’ve made it through this extensive guide on SEO techniques! By now, it’s clear that effective SEO in 2025 isn’t about one magic trick or hack – it’s about doing hundreds of little (and big) things right.
From researching the perfect keywords and crafting high-quality content, to tightening up your site’s technical performance and actively promoting your content for backlinks, SEO is truly a holistic endeavor.
The good news is, all these efforts work synergistically. For example, faster site speed not only pleases Google’s algorithm but also keeps visitors around longer (giving you better engagement signals).
Great content not only can rank on its own, but also naturally attracts links and social shares, boosting your off-page SEO. A strong backlink profile doesn’t just improve rankings – it can drive direct referral traffic and increase brand awareness.
In essence, each technique we discussed feeds into the others to create a robust, sustainable SEO strategy.
Here are a few final takeaways and action steps as you move forward:
1. Audit and Prioritize
It might be overwhelming to tackle all 60+ techniques at once. Start by auditing your site with the categories we used: Keywords/Content, On-Page, Technical, Off-Page. Identify your biggest weaknesses or missed opportunities.Prioritize fixes that will have the highest impact (for instance, if your site is slow and not mobile-friendly, address that ASAP as it affects every visitor and page).
2. Stay User-Focused
Whenever in doubt, think about the user experience first. Google’s algorithms increasingly emulate what makes users happy.If you provide valuable content, easy navigation, and fast, accessible pages, you’re aligning with what search engines want too. Every SEO trick should ultimately ladder up to a better user experience, not detract from it.
3. Be Consistent and Patient
SEO results take time. Implementing these techniques is like planting seeds, you need to water them (with ongoing optimization and content creation) and have patience for them to grow.Don’t be discouraged if you don’t see overnight changes in rankings. Typically, you’ll start noticing improvements in a few weeks to a few months, depending on your domain’s history and the competition.Keep the momentum: publish content regularly, keep building relationships for links, and always look for ways to improve existing pages.
4. Measure What Matters
Use tools to track your progress. Google Analytics will show you traffic growth and user engagement metrics. Google Search Console will show which queries you’re gaining impressions and clicks for, as well as any crawling/indexing issues.Rank tracking tools can help monitor your keyword positions (just remember that ranking is a means to an end – the end is traffic and conversions). By measuring, you can celebrate small wins and also adjust tactics if something isn’t working.
5. Adapt and Learn
The SEO landscape can change with a single algorithm update. Commit to staying informed, but also be agile.If an update hits you negatively, audit your site and content against Google’s guidelines (was it a quality issue? Page speed? Maybe low-quality backlinks?).Often, the answer is to double down on quality and clean up any questionable practices. Learning from your own site’s data is crucial; what works for one site might differ for another.SEO is part science, part art – your analytics are your laboratory, and your content is your creative canvas.
Finally, remember that SEO is just one part of building a successful online presence – but it’s a part that can amplify all your other marketing efforts.
The organic traffic you earn through these techniques is traffic you don’t have to pay for directly, and it can compound over time.
There’s a great sense of accomplishment in seeing your site climb the rankings through smart optimizations and knowing that you’re providing something of value to searchers out there.
Now it’s time to take action. Pick a few techniques from this guide and implement them today.
Maybe you’ll start by optimizing some title tags and meta descriptions, or doing a quick site speed win (like compressing images).
Maybe you’ll schedule a brainstorm meeting for new content ideas based on the keyword research tips, or reach out to a partner site about a guest post exchange. Every step counts.
By consistently applying the SEO strategies we’ve covered, you’ll gradually see your site rise in visibility, your traffic charts trend upward, and your business reap the rewards of increased organic reach. Keep at it, stay curious, and don’t be afraid to experiment.
Here’s to your SEO success in 2025 and beyond – now go implement these techniques and watch your website soar up the Google rankings. Good luck, and happy optimizing!






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)